What are two roles of glial cells
Home » » What are two roles of glial cellsYour What are two roles of glial cells images are ready. What are two roles of glial cells are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the What are two roles of glial cells files here. Get all royalty-free photos.
If you’re looking for what are two roles of glial cells pictures information related to the what are two roles of glial cells topic, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our site always provides you with hints for seeking the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly search and find more informative video articles and images that fit your interests.
What Are Two Roles Of Glial Cells. NG2 cells are a novel distinct class of central nervous system CNS glial cells characterized by the expression of the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan NG2. Therefore NG2-glia are also called oligodendrocyte precursor cells OPCs. Think of them as a secretarial pool for your nervous system plus the janitorial and maintenance staff. Oligodendrocytes are a specialized glial cell type in CNS that produce myelin which provides a protective sheath to the axons and improves the conduction velocity of signals between neurons.

Ependymal cells play a role in the blood-brain barrier. Glial cellderived neurotrophic factor GDNF is a mesenchyme-derived signaling factor that is a member of the transforming growth factor-β TGF-β family. Without them several of the most fundamental roles would never be achieved although they may not perform these roles themselves. This unique glial cell group has a typical function of proliferating and differentiating into oligodendrocytes during early development of the brain which is crucial to axon myelin formation. Another type of glial cell the ependymal cell form the linings of the brains internal cavities the ventricular system. A acting as insulation and providing structure to surrounding neurons Correct.
Oligodendrocytes are a specialized glial cell type in CNS that produce myelin which provides a protective sheath to the axons and improves the conduction velocity of signals between neurons.
Glial cellderived neurotrophic factor GDNF is a mesenchyme-derived signaling factor that is a member of the transforming growth factor-β TGF-β family. Remarkably glial cells can also have the opposite effect and impede synapse formation for example by preventing physical contact between neurons. Glial cells come in numerous forms each of which performs certain functions to keep the brain functioning properly or not in case of a neurological disease which affects the glial cells. Glial cells are capable of reproduction and when control over this capacity is lost primary brain tumors result. Think of them as a secretarial pool for your nervous system plus the janitorial and maintenance staff. The functions of neuroglia can be summarized in the maintenance of homeostasis in the nervous system metabolic support for neurons myelin formation destruction of pathogens removal of dead neurons and.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
As morphological physiological and biomolecular studies of NG2 cells have been conducted their roles have been gradually revealed. NG2 cells are a novel distinct class of central nervous system CNS glial cells characterized by the expression of the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan NG2. Glial cells come in numerous forms each of which performs certain functions to keep the brain functioning properly or not in case of a neurological disease which affects the glial cells. They may not do the big jobs but without them those big jobs would never get done. This unique glial cell group has a typical function of proliferating and differentiating into oligodendrocytes during early development of the brain which is crucial to axon myelin formation.
 Source: biologydictionary.net
Source: biologydictionary.net
The functions of neuroglia can be summarized in the maintenance of homeostasis in the nervous system metabolic support for neurons myelin formation destruction of pathogens removal of dead neurons and. It acts as the ligand for the RET receptor and induces growth of the ureteral bud during its interaction with the metanephric mesenchyme. Glial cells support neurons and maintain their environment. Think of them as a secretarial pool for your nervous system plus the janitorial and maintenance staff. This answer defines two roles of glial cells.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Glial cells come in numerous forms each of which performs certain functions to keep the brain functioning properly or not in case of a neurological disease which affects the glial cells. Primarily glial cells provide support for the neurons. Remarkably glial cells can also have the opposite effect and impede synapse formation for example by preventing physical contact between neurons. Another type of glial cell the ependymal cell form the linings of the brains internal cavities the ventricular system. Glial cells come in numerous forms each of which performs certain functions to keep the brain functioning properly or not in case of a neurological disease which affects the glial cells.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Without them several of the most fundamental roles would never be achieved although they may not perform these roles themselves. Ependymal cells play a role in the blood-brain barrier. Another type of glial cell the ependymal cell form the linings of the brains internal cavities the ventricular system. In vivo studies showed that decreased glial ensheathment of cerebellar PCs enhances the number of synaptic inputs 96 97. Glial cells commonly offer support to the neurons.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
In addition knowledge of how other glial cells are involved in neuropsychological disorders especially in the TH-sensitive regions of the brain Fonseca et al 2013 needs to be considered. Glial cells come in numerous forms each of which performs certain functions to keep the brain functioning properly or not in case of a neurological disease which affects the glial cells. This answer defines two roles of glial cells. They may not do the big jobs but without them those big jobs would never get done. The functions of neuroglia can be summarized in the maintenance of homeostasis in the nervous system metabolic support for neurons myelin formation destruction of pathogens removal of dead neurons and.
 Source: id.pinterest.com
Source: id.pinterest.com
It acts as the ligand for the RET receptor and induces growth of the ureteral bud during its interaction with the metanephric mesenchyme. Primarily glial cells provide support for the neurons. They were discovered in 1856 by physician Rudolf Virchow while investigating brain tissue. In addition to the undoubted supporting role glial cells have many other functions including the role in building the myelin sheath around the axon in the CNS oligodendrocytes and in the PNS Schwann cells participating in healing processes after brain injury maintaining ion homeostasis especially K ions and pH of extracellular fluid synthesizing the precursors of some neurotransmitters such as glutamine glutamate chemical mediator precursor and the role of being brain. While glia are often thought of as the supporting cast of the nervous system the number of glial cells in the brain actually outnumbers the number of neurons by a factor of ten.
 Source: qbi.uq.edu.au
Source: qbi.uq.edu.au
They were discovered in 1856 by physician Rudolf Virchow while investigating brain tissue. This barrier prevents the entry of certain usually large molecules into the central nervous system. They have been detected in a variety of human CNS diseases. Neurons would be unable to function without the vital roles that are fulfilled by these glial cells. Glial cellderived neurotrophic factor GDNF is a mesenchyme-derived signaling factor that is a member of the transforming growth factor-β TGF-β family.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Glial cells support neurons and maintain their environment. Glial cells come in numerous forms each of which performs certain functions to keep the brain functioning properly or not in case of a neurological disease which affects the glial cells. Glial cells support neurons and maintain their environment. Without them several of the most fundamental roles would never be achieved although they may not perform these roles themselves. While glia are often thought of as the supporting cast of the nervous system the number of glial cells in the brain actually outnumbers the number of neurons by a factor of ten.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
They have been detected in a variety of human CNS diseases. Without them several of the most fundamental roles would never be achieved although they may not perform these roles themselves. This barrier prevents the entry of certain usually large molecules into the central nervous system. Primarily glial cells provide support for the neurons. Oligodendrocytes are a specialized glial cell type in CNS that produce myelin which provides a protective sheath to the axons and improves the conduction velocity of signals between neurons.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
This unique glial cell group has a typical function of proliferating and differentiating into oligodendrocytes during early development of the brain which is crucial to axon myelin formation. Oligodendrocytes are a specialized glial cell type in CNS that produce myelin which provides a protective sheath to the axons and improves the conduction velocity of signals between neurons. This unique glial cell group has a typical function of proliferating and differentiating into oligodendrocytes during early development of the brain which is crucial to axon myelin formation. In vivo studies showed that decreased glial ensheathment of cerebellar PCs enhances the number of synaptic inputs 96 97. Oligodendrocytes form the myelin sheath around axons.
 Source: biologydictionary.net
Source: biologydictionary.net
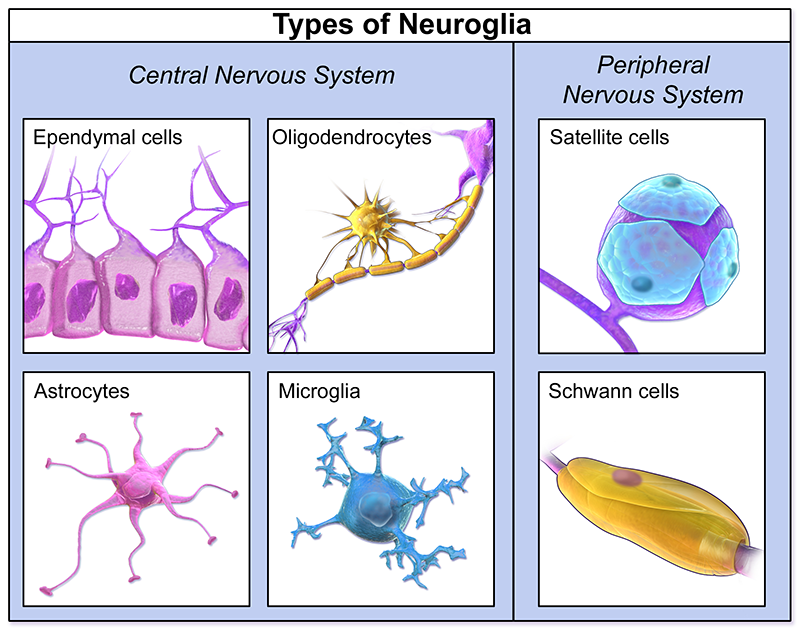
Glial cells of the a central nervous system include oligodendrocytes astrocytes ependymal cells and microglial cells. This barrier prevents the entry of certain usually large molecules into the central nervous system. NG2 cells are a novel distinct class of central nervous system CNS glial cells characterized by the expression of the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan NG2. Oligodendrocytes form the myelin sheath around axons. Primarily glial cells provide support for the neurons.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Glial cells of the a central nervous system include oligodendrocytes astrocytes ependymal cells and microglial cells. This barrier prevents the entry of certain usually large molecules into the central nervous system. Glial cells are capable of reproduction and when control over this capacity is lost primary brain tumors result. Oligodendrocytes form the myelin sheath around axons. Therefore NG2-glia are also called oligodendrocyte precursor cells OPCs.
 Source: faculty.washington.edu
Source: faculty.washington.edu
Glial cells of the a central nervous system include oligodendrocytes astrocytes ependymal cells and microglial cells. This barrier prevents the entry of certain usually large molecules into the central nervous system. This unique glial cell group has a typical function of proliferating and differentiating into oligodendrocytes during early development of the brain which is crucial to axon myelin formation. In addition to the undoubted supporting role glial cells have many other functions including the role in building the myelin sheath around the axon in the CNS oligodendrocytes and in the PNS Schwann cells participating in healing processes after brain injury maintaining ion homeostasis especially K ions and pH of extracellular fluid synthesizing the precursors of some neurotransmitters such as glutamine glutamate chemical mediator precursor and the role of being brain. While glia are often thought of as the supporting cast of the nervous system the number of glial cells in the brain actually outnumbers the number of neurons by a factor of ten.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Oligodendrocytes are a specialized glial cell type in CNS that produce myelin which provides a protective sheath to the axons and improves the conduction velocity of signals between neurons. This answer defines two roles of glial cells. The functions of neuroglia can be summarized in the maintenance of homeostasis in the nervous system metabolic support for neurons myelin formation destruction of pathogens removal of dead neurons and. They have been detected in a variety of human CNS diseases. Glial cellderived neurotrophic factor GDNF is a mesenchyme-derived signaling factor that is a member of the transforming growth factor-β TGF-β family.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Think of them as a secretarial pool for your nervous system plus the janitorial and maintenance staff. This barrier prevents the entry of certain usually large molecules into the central nervous system. A acting as insulation and providing structure to surrounding neurons Correct. Another type of glial cell the ependymal cell form the linings of the brains internal cavities the ventricular system. Glial cells come in numerous forms each of which performs certain functions to keep the brain functioning properly or not in case of a neurological disease which affects the glial cells.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Glial cells come in numerous forms each of which performs certain functions to keep the brain functioning properly or not in case of a neurological disease which affects the glial cells. The glia glial cells or simply glia are the whole cell nonneuronal of the nervous system. This answer defines two roles of glial cells. This barrier prevents the entry of certain usually large molecules into the central nervous system. Glial cells come in numerous forms each of which performs certain functions to keep the brain functioning properly or not in case of a neurological disease which affects the glial cells.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Oligodendrocytes are a specialized glial cell type in CNS that produce myelin which provides a protective sheath to the axons and improves the conduction velocity of signals between neurons. Therefore NG2-glia are also called oligodendrocyte precursor cells OPCs. As morphological physiological and biomolecular studies of NG2 cells have been conducted their roles have been gradually revealed. What are two roles of glial cells. A acting as insulation and providing structure to surrounding neurons Correct.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
NG2 cells are a novel distinct class of central nervous system CNS glial cells characterized by the expression of the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan NG2. They have been detected in a variety of human CNS diseases. In addition to the undoubted supporting role glial cells have many other functions including the role in building the myelin sheath around the axon in the CNS oligodendrocytes and in the PNS Schwann cells participating in healing processes after brain injury maintaining ion homeostasis especially K ions and pH of extracellular fluid synthesizing the precursors of some neurotransmitters such as glutamine glutamate chemical mediator precursor and the role of being brain. Without them several of the most fundamental roles would never be achieved although they may not perform these roles themselves. Glial cells of the a central nervous system include oligodendrocytes astrocytes ependymal cells and microglial cells.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title what are two roles of glial cells by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.