Vibrio cholerae anaerobic or aerobic
Home » » Vibrio cholerae anaerobic or aerobicYour Vibrio cholerae anaerobic or aerobic images are ready. Vibrio cholerae anaerobic or aerobic are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Vibrio cholerae anaerobic or aerobic files here. Find and Download all royalty-free photos.
If you’re searching for vibrio cholerae anaerobic or aerobic pictures information related to the vibrio cholerae anaerobic or aerobic keyword, you have pay a visit to the right blog. Our website frequently gives you hints for seeking the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and find more enlightening video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
Vibrio Cholerae Anaerobic Or Aerobic. Members of the genus Vibrio are facultatively anaerobic asporogenous motile curved or straight gram-negative rods. Verma Khanna and Chawla A comma-shaped gram-negative aerobic or facultatively anaerobic bacillus that varies in size from 1-3 µm. Data are displayed as the fold induction in cultures grown an-aerobically over those grown aerobically. Vibrio cholerae a member of the family Vibrionaceae is a facultatively anaero- bic Gram-negative non-spore-forming curved rod about 1426mm long capable of respiratory and fermentative metabolism.
 Genetic Dissection Of The Fermentative And Respiratory Contributions Supporting Vibrio Cholerae Hypoxic Growth Biorxiv From biorxiv.org
Genetic Dissection Of The Fermentative And Respiratory Contributions Supporting Vibrio Cholerae Hypoxic Growth Biorxiv From biorxiv.org
Vibrio cholerae is a bacterial pathogen that replicates to high cell density in the small intestine of human hosts leading to the diarrheal disease cholera. That under aerobic conditions very few bacterial cells were visible on the intestinal surface Fig. Data are displayed as the fold induction in cultures grown an-aerobically over those grown aerobically. Phenomenon actually facilitates V. Compare and contrast aerobic and anaerobic respiration. For example the gram-negative opportunist Pseudomonas aeruginosa and the gram-negative cholera-causing Vibrio cholerae use cytochrome c oxidase which can be detected by the oxidase test.
The ability of V.
DiRita aDepartmentofMicrobiologyMolecularGeneticsMichiganStateUniversityEastLansingMichiganUSA ABSTRACT Vibrio cholerae replicates to high cell density in the human small intes-tine leading to the. Phenomenon actually facilitates V. Aerobic Metabolism in Vibrio cholerae Is Required for Population Expansion during Infection Andrew J. Cholerae may exploit the thiol-based regulatory switch to cope with its two lifestyles survival in aquatic environments aerobic and colonization of the human intestine anaerobic to microaerophilic. In this work we focus on DPO. Cholerae cultured under anaerobic conditions does not produce CAI-1 whereas increased DPO production does occur.
 Source: microbewiki.kenyon.edu
Source: microbewiki.kenyon.edu
Vibrio cholerae a member of the family Vibrionaceae is a facultatively anaero- bic Gram-negative non-spore-forming curved rod about 1426mm long capable of respiratory and fermentative metabolism. One of the signals sensed by V. For example the gram-negative opportunist Pseudomonas aeruginosa and the gram-negative cholera-causing Vibrio cholerae use cytochrome c oxidase which can be detected by the oxidase test. Cholerae is highly promoted during anaerobic growth using trimethylamine N-oxide TMAO as an alternative electron acceptor. Vibrio cholerae is a bacterial pathogen that replicates to high cell density in the small intestine of human hosts leading to the diarrheal disease cholera.
 Source: biologyease.com
Source: biologyease.com
That under aerobic conditions very few bacterial cells were visible on the intestinal surface Fig. The adherence required TCP because a tcpA mutant failed to attach to intestines even under anaerobic. It is well defined on the basis. For example the gram-negative opportunist Pseudomonas aeruginosa and the gram-negative cholera-causing Vibrio cholerae use cytochrome c oxidase which can be detected by the oxidase test. In this work we focus on DPO.
 Source: microbe-canvas.com
Source: microbe-canvas.com
We demonstrate that oxidative metabolism is a key contributor to the replicative success of V. For example the gram-negative opportunist Pseudomonas aeruginosa and the gram-negative cholera-causing Vibrio cholerae use cytochrome c oxidase which can be detected by the oxidase test. It is well defined on the basis. Verma Khanna and Chawla A comma-shaped gram-negative aerobic or facultatively anaerobic bacillus that varies in size from 1-3 µm. Cholerae attached efficiently Fig.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
We show that the VqmA-DPO complex more strongly activates target gene expression under anaerobic than aerobic conditions. Vibrios either require NaCl or have their growth stimulated by its. Choleraeto colonize and cause disease requires the intricately regulated expression of a number of virulence factors during infection. In this work we focus on DPO. Cholerae cultured under anaerobic conditions does not produce CAI-1 whereas increased DPO production does occur.
 Source: medscape.com
Source: medscape.com
Vibrio cholerae a member of the family Vibrionaceae is a facultatively anaero- bic Gram-negative non-spore-forming curved rod about 1426mm long capable of respiratory and fermentative metabolism. Killed WC variants of the vaccine that contain both Vibrio cholerae O1 and O139 provides 50 protection for 3 years. Compare and contrast aerobic and anaerobic respiration. That under aerobic conditions very few bacterial cells were visible on the intestinal surface Fig. As a facultative anaerobe Vibrio cholerae can grow by anaerobic respiration.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Choleraeto colonize and cause disease requires the intricately regulated expression of a number of virulence factors during infection. We find that V. The adherence required TCP because a tcpA mutant failed to attach to intestines even under anaerobic. It is well defined on the basis. In our study we found that the extent of in-vivo nitration is negatively correlated with the intracellular nitrite content and maximum nitration occurs during log phase of V.
 Source: biorxiv.org
Source: biorxiv.org
V cholerae is a comma-shaped gram-negative aerobic or facultatively anaerobic bacillus that varies in size from 1-3 µm in length by 05-08. Cholerae in vivo using an infant mouse model in which PDH mutants were attenuated 100-fold relative to the wild. As a facultative anaerobe Vibrio cholerae can grow by anaerobic respiration. Vibrio cholerae is a bacterial pathogen that replicates to high cell density in the small intestine of human hosts leading to the diarrheal disease cholera. Choleraeto colonize and cause disease requires the intricately regulated expression of a number of virulence factors during infection.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Van Alst aVictor J. Cholerae cell survival in anaerobic or hypoxic condition. Aerobic Metabolism in Vibrio cholerae Is Required for Population Expansion during Infection Andrew J. The ability of V. By disrupting the pyruvate dehydrogenase PDH complex and pyruvate formate-lyase PFL we could differentiate aerobic and anaerobic metabolic pathway involvement in V.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The ability of V. Vibrio cholerae a member of the family Vibrionaceae is a facultatively anaero- bic Gram-negative non-spore-forming curved rod about 1426mm long capable of respiratory and fermentative metabolism. Cholerae cell survival in anaerobic or hypoxic condition. As a facultative anaerobe Vibrio cholerae can grow by anaerobic respiration. Cholerae senses and responds to environmental signals that govern cellular responses.

Cholerae senses and responds to environmental signals that govern cellular responses. Vibrios either require NaCl or have their growth stimulated by its. That under aerobic conditions very few bacterial cells were visible on the intestinal surface Fig. Verma Khanna and Chawla A comma-shaped gram-negative aerobic or facultatively anaerobic bacillus that varies in size from 1-3 µm. Cholerae attached efficiently Fig.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Cholerae in vivo using an infant mouse model in which PDH mutants were attenuated 100-fold relative to the wild. Verma Khanna and Chawla A comma-shaped gram-negative aerobic or facultatively anaerobic bacillus that varies in size from 1-3 µm. Cholerae cell survival in anaerobic or hypoxic condition. V cholerae is a comma-shaped gram-negative aerobic or facultatively anaerobic bacillus that varies in size from 1-3 µm in length by 05-08. That under aerobic conditions very few bacterial cells were visible on the intestinal surface Fig.
 Source: basicmedicalkey.com
Source: basicmedicalkey.com
Cholerae containing the indicated luxCDABE transcriptional reporter plasmids were grown under aerobic and anaerobic conditions in AKI me-dium at 37 C until OD 600 reached 02 at which point luminescence was measured. Vibrio cholerae a member of the family Vibrionaceae is a facultatively anaero- bic Gram-negative non-spore-forming curved rod about 1426mm long capable of respiratory and fermentative metabolism. Aerobic Metabolism in Vibrio cholerae Is Required for Population Expansion during Infection Andrew J. Choleraeto colonize and cause disease requires the intricately regulated expression of a number of virulence factors during infection. For example the gram-negative opportunist Pseudomonas aeruginosa and the gram-negative cholera-causing Vibrio cholerae use cytochrome c oxidase which can be detected by the oxidase test.
 Source: biorxiv.org
Source: biorxiv.org
Vibrio cholerae is a bacterial pathogen that replicates to high cell density in the small intestine of human hosts leading to the diarrheal disease cholera. For example the gram-negative opportunist Pseudomonas aeruginosa and the gram-negative cholera-causing Vibrio cholerae use cytochrome c oxidase which can be detected by the oxidase test. We demonstrate that oxidative metabolism is a key contributor to the replicative success of V. Vibrio cholerae is a bacterial pathogen that replicates to high cell density in the small intestine of human hosts leading to the diarrheal disease cholera. The ability of V.
 Source: biorxiv.org
Source: biorxiv.org
In our study we found that the extent of in-vivo nitration is negatively correlated with the intracellular nitrite content and maximum nitration occurs during log phase of V. 1C Left whereas without oxygen wild-type WT V. By disrupting the pyruvate dehydrogenase PDH complex and pyruvate formate-lyase PFL we could differentiate aerobic and anaerobic metabolic pathway involvement in V. Production of cholera toxin CT a major virulence factor of V. Cholerae is highly promoted during anaerobic growth using trimethylamine N-oxide TMAO as an alternative electron acceptor.
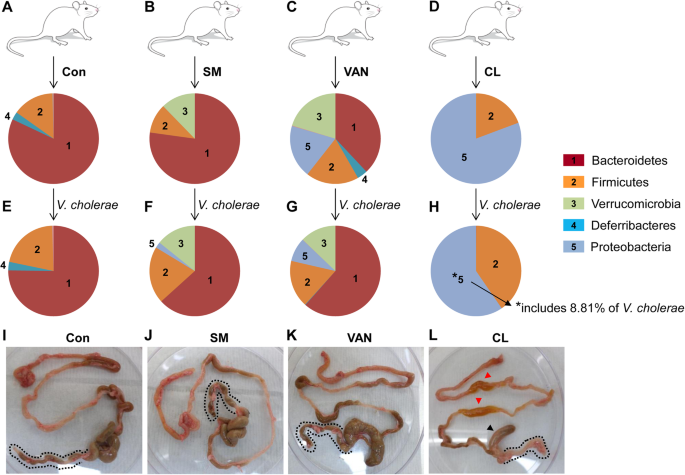 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
Compare and contrast aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Vibrio cholerae anaerobic induction of virulence gene expression is controlled by thiol-based switches of virulence regulator AphB. Compare and contrast aerobic and anaerobic respiration. We show that the VqmA-DPO complex more strongly activates target gene expression under anaerobic than aerobic conditions. Choleraeis the presence of.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
The adherence required TCP because a tcpA mutant failed to attach to intestines even under anaerobic. We show that the VqmA-DPO complex more strongly activates target gene expression under anaerobic than aerobic conditions. Cholerae senses and responds to environmental signals that govern cellular responses. V cholerae is a comma-shaped gram-negative aerobic or facultatively anaerobic bacillus that varies in size from 1-3 µm in length by 05-08. Aerobic Metabolism in Vibrio cholerae Is Required for Population Expansion during Infection Andrew J.
 Source: europepmc.org
Source: europepmc.org
Cholerae senses and responds to environmental signals that govern cellular responses. V cholerae is a comma-shaped gram-negative aerobic or facultatively anaerobic bacillus that varies in size from 1-3 µm in length by 05-08. Members of the genus Vibrio are facultatively anaerobic asporogenous motile curved or straight gram-negative rods. Cholerae may exploit the thiol-based regulatory switch to cope with its two lifestyles survival in aquatic environments aerobic and colonization of the human intestine anaerobic to microaerophilic. We demonstrate that oxidative metabolism is a key contributor to the replicative success of V.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
1C Left whereas without oxygen wild-type WT V. In this work we focus on DPO. Vibrio cholerae anaerobic induction of virulence gene expression is controlled by thiol-based switches of virulence regulator AphB. 1C Left whereas without oxygen wild-type WT V. Choleraeis the presence of.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title vibrio cholerae anaerobic or aerobic by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.