Toxin antitoxin system
Home » » Toxin antitoxin systemYour Toxin antitoxin system images are ready. Toxin antitoxin system are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Toxin antitoxin system files here. Find and Download all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for toxin antitoxin system images information connected with to the toxin antitoxin system topic, you have visit the ideal blog. Our site always gives you suggestions for refferencing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more enlightening video articles and images that match your interests.
Toxin Antitoxin System. If a cell loses the mobile genetic element with the toxinantitoxin system the production of the antitoxin is. Nine hypothetical biological functions of TA systems have been proposed 24 including growth control persister formation antiphage measures 28 and general stress response. Toxinantitoxin TA systems are composed of a set of closely linked genes that encode a stable toxin and an unstable antitoxin that protects the cell against the effects of the toxin as long as it is stable. The antitoxin acts as an unexpected player in the negative control of plasmid replication.
 Artificial Activation Of Toxin Antitoxin Systems As An Antibacterial Strategy Trends In Microbiology From cell.com
Artificial Activation Of Toxin Antitoxin Systems As An Antibacterial Strategy Trends In Microbiology From cell.com
Type II toxin-antitoxin TA systems are small genetic elements composed of a toxic protein and its cognate antitoxin protein the latter counteracting the toxicity of the former. The toxin-antitoxin TA system-related research is an evolving field. The cells must therefore continue to synthesise the antitoxin in order to avoid poisoning by the toxin. Toxinantitoxin TA systems are composed of a set of closely linked genes that encode a stable toxin and an unstable antitoxin that protects the cell against the effects of the toxin as long as it is stable. The role of toxin-antitoxin TA systems in cell physiology is enigmatic. This system has been observed in multiple prokaryotic organisms.
Toxin-antitoxin TA systems are small genetic elements found in the majority of prokaryotes.
The typical toxin-antitoxin TA system consists of a stable toxin and an unstable antitoxin and is widely distributed in bacterial genomes. Toxinantitoxin TA systems are composed of a set of closely linked genes that encode a stable toxin and an unstable antitoxin that protects the cell against the effects of the toxin as long as it is stable. Type II toxin-antitoxin TA systems are small genetic elements composed of a toxic protein and its cognate antitoxin protein the latter counteracting the toxicity of the former. Type II toxin-antitoxin TA systems are small genetic elements composed of a toxic protein and its cognate antitoxin protein the latter counteracting the toxicity of the former. The role of toxin-antitoxin TA systems in cell physiology is enigmatic. Toxinantitoxin TA systems are present in most prokaryote genomes.
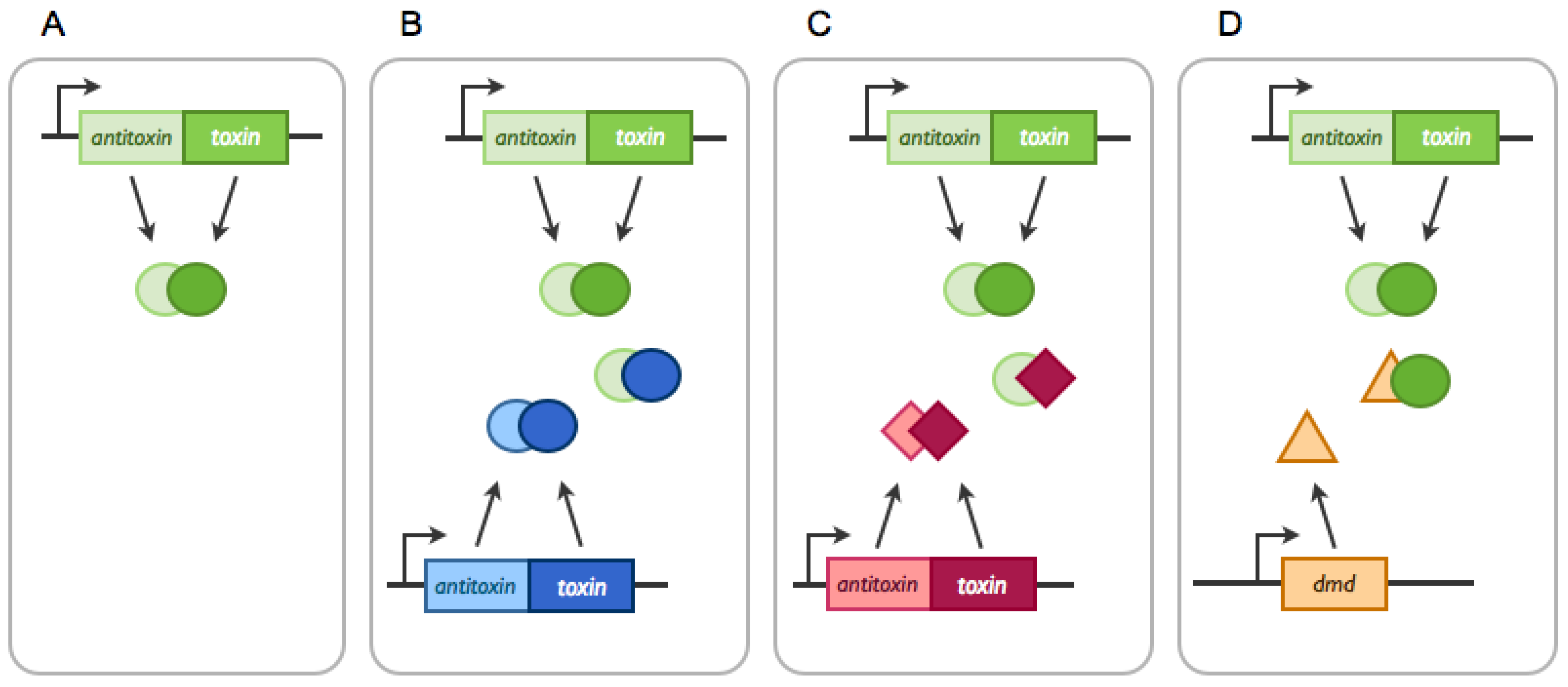 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Last year Gerdes and colleagues published a paper describing experiments that failed to support earlier work from their group 2 3 which had implicated 10 type II toxin-antitoxin TA systems in the formation of antibiotic-tolerant Escherichia coli K-12 persister cellsThe problem apparently arose as a result of contamination by and activation of the cryptic bacteriophage Φ80 in. Toxin-antitoxin TA systems typically consist of two genes in an operon which encode a stable toxin that disrupts an essential cellular process eg translation via mRNA degradation and a labile antitoxin either RNA or a protein that prevents toxicity RNA antitoxins are known as type I if they inhibit toxin translation as antisense RNA or type III if they inhibit toxin. However the antitoxin molecules are perfidiously eliminated faster through the cellular degradation mechanisms than the toxin. While TA systems were initially discovered on plasmids functioning as addiction modules through a phenomenon called postsegregational killing they were later shown to be massively present in bacterial chromosomes. The role of toxin-antitoxin TA systems in cell physiology is enigmatic.
 Source: biooekonomie-bw.de
Source: biooekonomie-bw.de
Nine hypothetical biological functions of TA systems have been proposed 24 including growth control persister formation antiphage measures 28 and general stress response. Toxinantitoxin TA systems are composed of a set of closely linked genes that encode a stable toxin and an unstable antitoxin that protects the cell against the effects of the toxin as long as it is stable. The toxin and antitoxin form a conjugative pair of genes that. While TA systems were initially discovered on plasmids functioning as addiction modules through a phenomenon called postsegregational killing they were later shown to be massively present in bacterial chromosomes. Here we demonstrate the functional significance of a large group of antitoxins on conjugative plasmids.
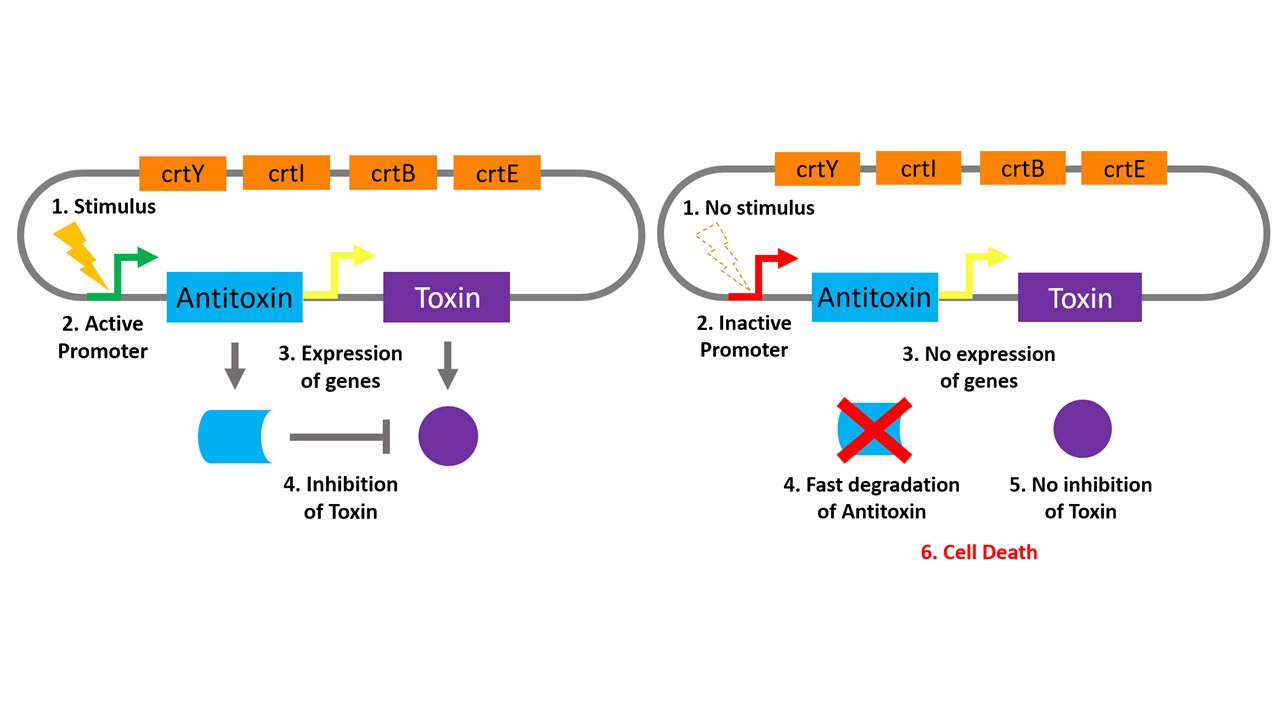 Source: 2016.igem.org
Source: 2016.igem.org
The typical toxin-antitoxin TA system consists of a stable toxin and an unstable antitoxin and is widely distributed in bacterial genomes. They encode toxin proteins that interfere with vital cellular functions and are counteracted by antitoxins. Classical toxinantitoxin TA systems are based on silencing of a stable toxin by a labile antitoxin that when inactivated releases the toxin resulting in a reduction in metabolism. Nine hypothetical biological functions of TA systems have been proposed 24 including growth control persister formation antiphage measures 28 and general stress response. Toxins are almost exclusively proteins that reduce metabolism but do not cause cell death and antitoxins are either RNA or proteins that counteract the toxin or the RNA that encodes it.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
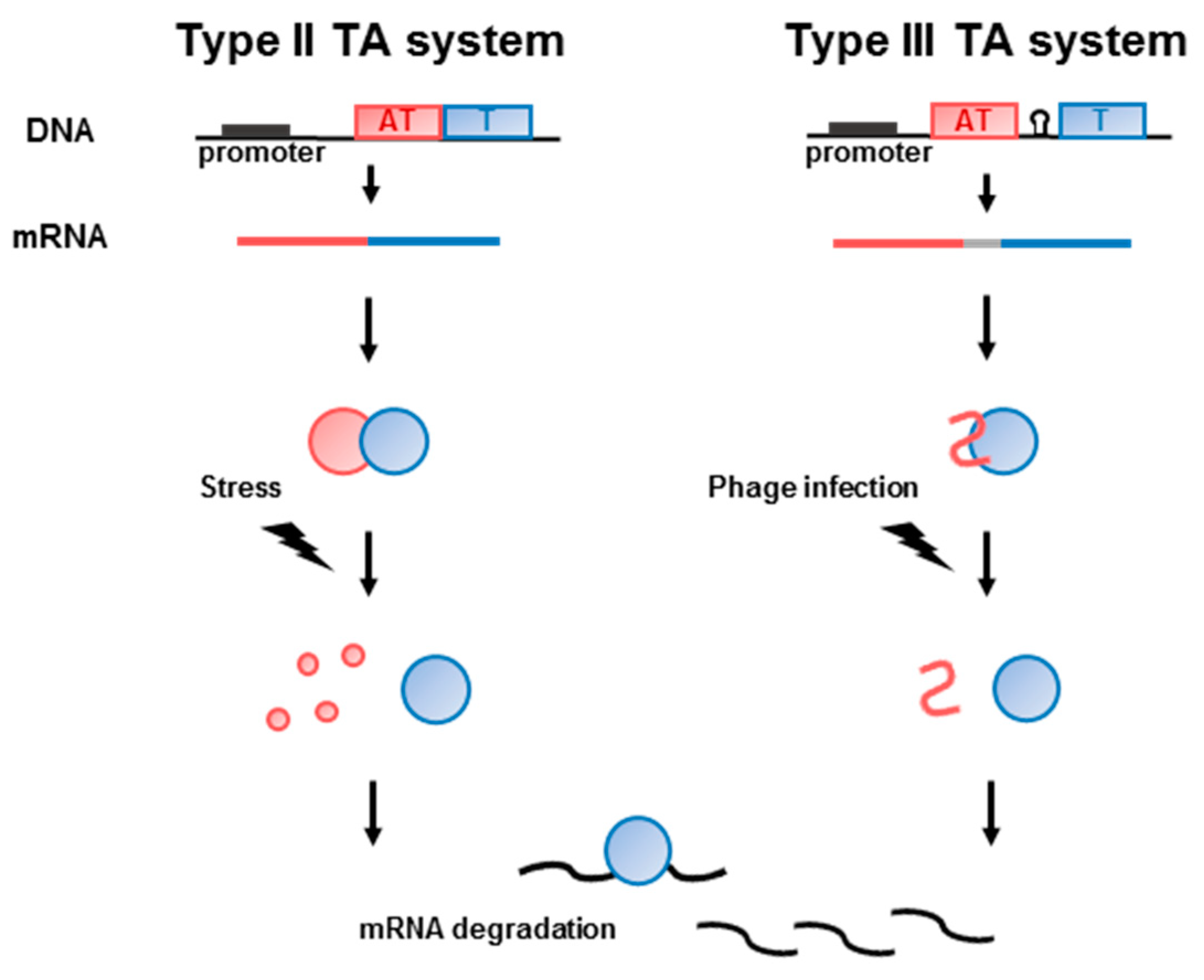
The antitoxin RNA mimics a CRISPR RNA and repurposes the CRISPR immunity effector to transcriptionally repress a toxin RNA that would otherwise arrest. Toxin-antitoxin TA systems typically consist of two genes in an operon which encode a stable toxin that disrupts an essential cellular process eg translation via mRNA degradation and a labile antitoxin either RNA or a protein that prevents toxicity RNA antitoxins are known as type I if they inhibit toxin translation as antisense RNA or type III if they inhibit toxin. Bacterial toxinantitoxin TA systems are diverse and widespread in the prokaryotic kingdom. The cells must therefore continue to synthesise the antitoxin in order to avoid poisoning by the toxin. Here we demonstrate the functional significance of a large group of antitoxins on conjugative plasmids.
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
Type II toxin-antitoxin TA systems are small genetic elements composed of a toxic protein and its cognate antitoxin protein the latter counteracting the toxicity of the former. Last year Gerdes and colleagues published a paper describing experiments that failed to support earlier work from their group 2 3 which had implicated 10 type II toxin-antitoxin TA systems in the formation of antibiotic-tolerant Escherichia coli K-12 persister cellsThe problem apparently arose as a result of contamination by and activation of the cryptic bacteriophage Φ80 in. The cells must therefore continue to synthesise the antitoxin in order to avoid poisoning by the toxin. The toxin-antitoxin TA system-related research is an evolving field. Classical toxinantitoxin TA systems are based on silencing of a stable toxin by a labile antitoxin that when inactivated releases the toxin resulting in a reduction in metabolism.

Dependent on the chemical nature of the antitoxins protein or RNA and how they control the activ. The role of toxin-antitoxin TA systems in cell physiology is enigmatic. Type II toxin-antitoxin TA systems are small genetic elements composed of a toxic protein and its cognate antitoxin protein the latter counteracting the toxicity of the former. However the antitoxin molecules are perfidiously eliminated faster through the cellular degradation mechanisms than the toxin. The typical toxin-antitoxin TA system consists of a stable toxin and an unstable antitoxin and is widely distributed in bacterial genomes.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
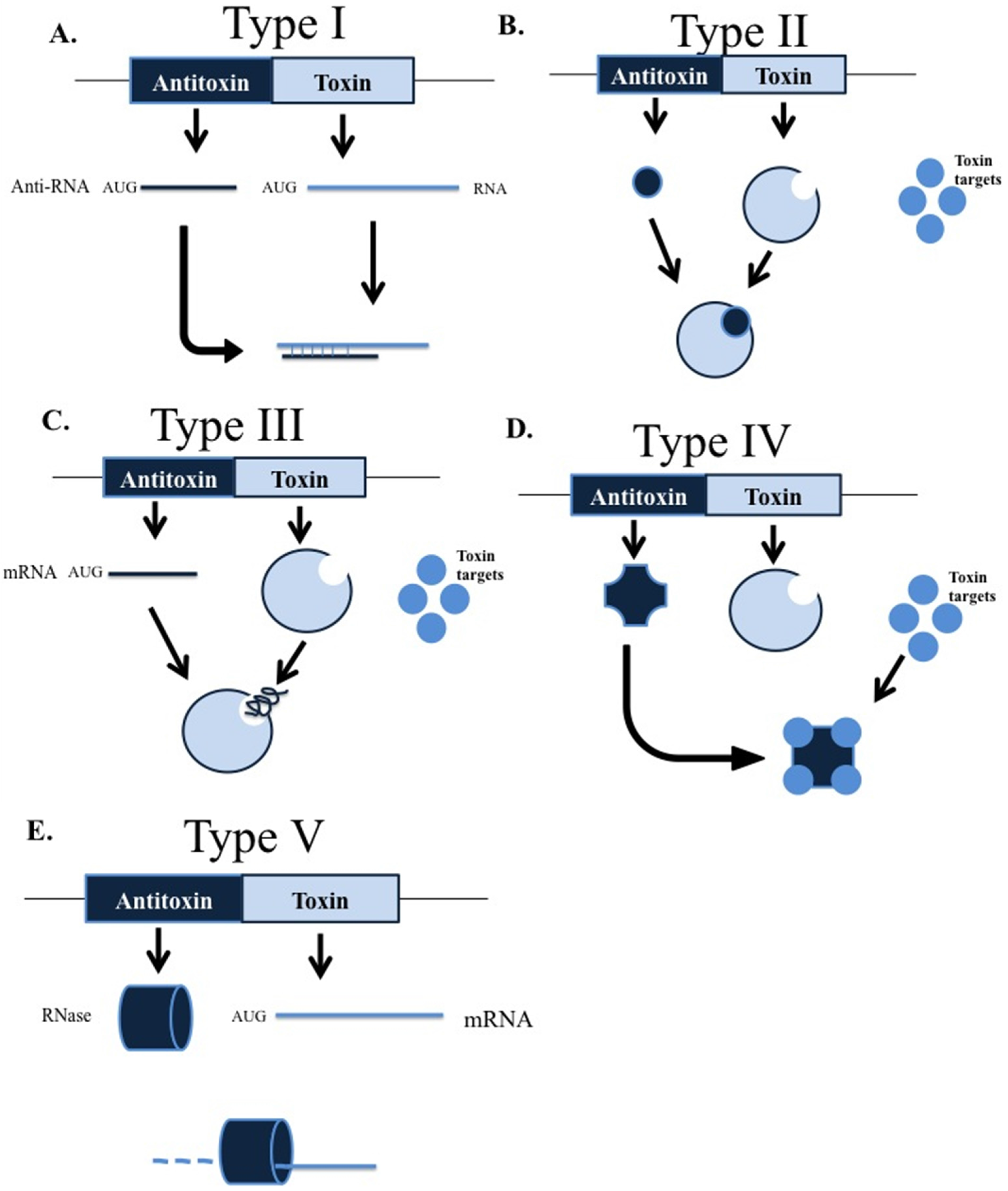
Toxin-antitoxin TA systems typically consist of two genes in an operon which encode a stable toxin that disrupts an essential cellular process eg translation via mRNA degradation and a labile antitoxin either RNA or a protein that prevents toxicity RNA antitoxins are known as type I if they inhibit toxin translation as antisense RNA or type III if they inhibit toxin. Dependent on the chemical nature of the antitoxins protein or RNA and how they control the activ. While the product of the toxin gene is typically a protein that of the antitoxin gene is either a noncoding RNA in TA systems I and III or a low-molecular-weight protein in TA systems II IV V. While TA systems were initially discovered on plasmids functioning as addiction modules through a phenomenon called postsegregational killing they were later shown to be massively present in bacterial chromosomes. Toxin-antitoxin TA systems or small genetic elements found in the chromosomes of bacteria allow bacteria to either speed up growth using antitoxins or slow down growth using toxins in order to thrive in periods where food is either plentiful or scarce.
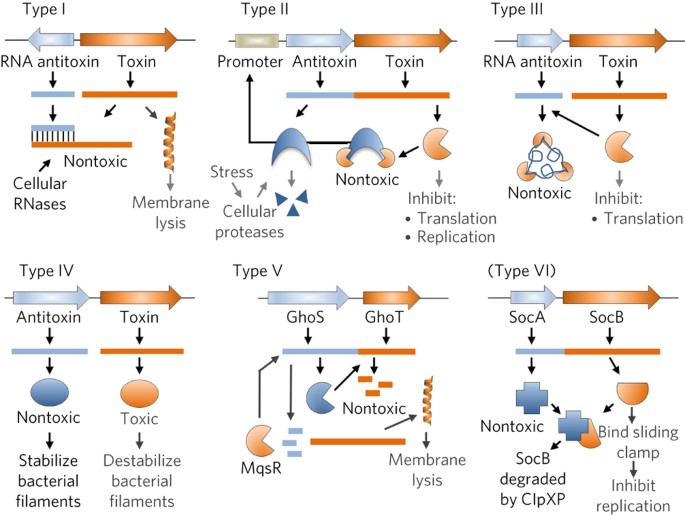 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
The typical toxin-antitoxin TA system consists of a stable toxin and an unstable antitoxin and is widely distributed in bacterial genomes. However the antitoxin molecules are perfidiously eliminated faster through the cellular degradation mechanisms than the toxin. Toxin-antitoxin TA systems typically consist of two genes in an operon which encode a stable toxin that disrupts an essential cellular process eg translation via mRNA degradation and a labile antitoxin either RNA or a protein that prevents toxicity RNA antitoxins are known as type I if they inhibit toxin translation as antisense RNA or type III if they inhibit toxin. Dependent on the chemical nature of the antitoxins protein or RNA and how they control the activ. This system has been observed in multiple prokaryotic organisms.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
While the product of the toxin gene is typically a protein that of the antitoxin gene is either a noncoding RNA in TA systems I and III or a low-molecular-weight protein in TA systems II IV V. The cells must therefore continue to synthesise the antitoxin in order to avoid poisoning by the toxin. The toxin and antitoxin form a conjugative pair of genes that. Toxinantitoxin TA systems are one of the conserved modules on conjugative plasmids. The antitoxin RNA mimics a CRISPR RNA and repurposes the CRISPR immunity effector to transcriptionally repress a toxin RNA that would otherwise arrest.
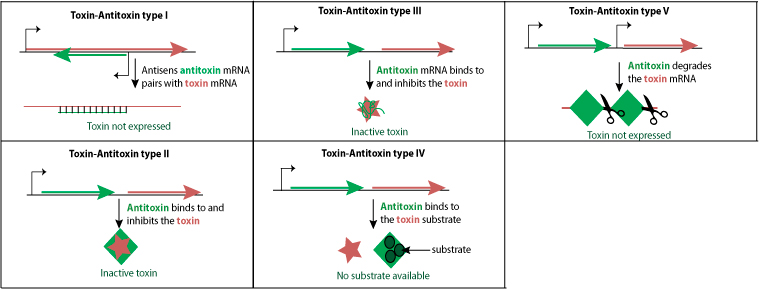 Source: viralzone.expasy.org
Source: viralzone.expasy.org
The typical toxin-antitoxin TA system consists of a stable toxin and an unstable antitoxin and is widely distributed in bacterial genomes. Toxin-antitoxin TA systems are small genetic elements found in the majority of prokaryotes. This system has been observed in multiple prokaryotic organisms. Last year Gerdes and colleagues published a paper describing experiments that failed to support earlier work from their group 2 3 which had implicated 10 type II toxin-antitoxin TA systems in the formation of antibiotic-tolerant Escherichia coli K-12 persister cellsThe problem apparently arose as a result of contamination by and activation of the cryptic bacteriophage Φ80 in. Toxins are almost exclusively proteins that reduce metabolism but do not cause cell death and antitoxins are either RNA or proteins that counteract the toxin or the RNA that encodes it.
 Source: pfam.xfam.org
Source: pfam.xfam.org
If a cell loses the mobile genetic element with the toxinantitoxin system the production of the antitoxin is. However the antitoxin molecules are perfidiously eliminated faster through the cellular degradation mechanisms than the toxin. Nine hypothetical biological functions of TA systems have been proposed 24 including growth control persister formation antiphage measures 28 and general stress response. Toxins are almost exclusively proteins that reduce metabolism but do not cause cell death and antitoxins are either RNA or proteins that counteract the toxin or the RNA that encodes it. Toxinantitoxin TA systems are one of the conserved modules on conjugative plasmids.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The antitoxin acts as an unexpected player in the negative control of plasmid replication. Toxin-antitoxin TA systems or small genetic elements found in the chromosomes of bacteria allow bacteria to either speed up growth using antitoxins or slow down growth using toxins in order to thrive in periods where food is either plentiful or scarce. Last year Gerdes and colleagues published a paper describing experiments that failed to support earlier work from their group 2 3 which had implicated 10 type II toxin-antitoxin TA systems in the formation of antibiotic-tolerant Escherichia coli K-12 persister cellsThe problem apparently arose as a result of contamination by and activation of the cryptic bacteriophage Φ80 in. Here we demonstrate the functional significance of a large group of antitoxins on conjugative plasmids. Classical toxinantitoxin TA systems are based on silencing of a stable toxin by a labile antitoxin that when inactivated releases the toxin resulting in a reduction in metabolism.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Bacterial toxinantitoxin TA systems are diverse and widespread in the prokaryotic kingdom. This system has been observed in multiple prokaryotic organisms. The toxin and antitoxin form a conjugative pair of genes that. The typical toxin-antitoxin TA system consists of a stable toxin and an unstable antitoxin and is widely distributed in bacterial genomes. Type II toxin-antitoxin TA systems are small genetic elements composed of a toxic protein and its cognate antitoxin protein the latter counteracting the toxicity of the former.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Toxinantitoxin TA systems are one of the conserved modules on conjugative plasmids. Toxin-antitoxin TA systems or small genetic elements found in the chromosomes of bacteria allow bacteria to either speed up growth using antitoxins or slow down growth using toxins in order to thrive in periods where food is either plentiful or scarce. Here we demonstrate the functional significance of a large group of antitoxins on conjugative plasmids. The toxin and antitoxin form a conjugative pair of genes that. While TA systems were initially discovered on plasmids functioning as addiction modules through a phenomenon called postsegregational killing they were later shown to be massively present in bacterial chromosomes.
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
Toxin-antitoxin TA systems or small genetic elements found in the chromosomes of bacteria allow bacteria to either speed up growth using antitoxins or slow down growth using toxins in order to thrive in periods where food is either plentiful or scarce. They are composed of closely linked genes encoding a stable toxin that can harm the host cell and its cognate labile antitoxin which protects the host from the toxins deleterious effect. Toxin-antitoxin TA systems typically consist of two genes in an operon which encode a stable toxin that disrupts an essential cellular process eg translation via mRNA degradation and a labile antitoxin either RNA or a protein that prevents toxicity RNA antitoxins are known as type I if they inhibit toxin translation as antisense RNA or type III if they inhibit toxin. However the antitoxin molecules are perfidiously eliminated faster through the cellular degradation mechanisms than the toxin. Toxinantitoxin TA systems are one of the conserved modules on conjugative plasmids.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Dependent on the chemical nature of the antitoxins protein or RNA and how they control the activ. The antitoxin acts as an unexpected player in the negative control of plasmid replication. The antitoxin RNA mimics a CRISPR RNA and repurposes the CRISPR immunity effector to transcriptionally repress a toxin RNA that would otherwise arrest. They are composed of closely linked genes encoding a stable toxin that can harm the host cell and its cognate labile antitoxin which protects the host from the toxins deleterious effect. The typical toxin-antitoxin TA system consists of a stable toxin and an unstable antitoxin and is widely distributed in bacterial genomes.
 Source: wikiwand.com
Source: wikiwand.com
Toxin-antitoxin TA systems typically consist of two genes in an operon which encode a stable toxin that disrupts an essential cellular process eg translation via mRNA degradation and a labile antitoxin either RNA or a protein that prevents toxicity RNA antitoxins are known as type I if they inhibit toxin translation as antisense RNA or type III if they inhibit toxin. The toxin is always of a protein nature while the antitoxin can be a protein or a non-coding RNA. Most of the TA modules in bacteria were discovered during the first decade of the current millennium and studies have indicated that TA genes are encoded on plasmids andor chromosomes of. This system has been observed in multiple prokaryotic organisms. The antitoxin acts as an unexpected player in the negative control of plasmid replication.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Dependent on the chemical nature of the antitoxins protein or RNA and how they control the activ. The toxin-antitoxin TA system-related research is an evolving field. If a cell loses the mobile genetic element with the toxinantitoxin system the production of the antitoxin is. The toxin is always of a protein nature while the antitoxin can be a protein or a non-coding RNA. Here we demonstrate the functional significance of a large group of antitoxins on conjugative plasmids.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title toxin antitoxin system by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.