Mussels that live near a deep sea vent
Home » » Mussels that live near a deep sea ventYour Mussels that live near a deep sea vent images are available. Mussels that live near a deep sea vent are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Mussels that live near a deep sea vent files here. Download all royalty-free images.
If you’re looking for mussels that live near a deep sea vent images information linked to the mussels that live near a deep sea vent topic, you have pay a visit to the right site. Our website always provides you with hints for refferencing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and locate more enlightening video content and graphics that match your interests.
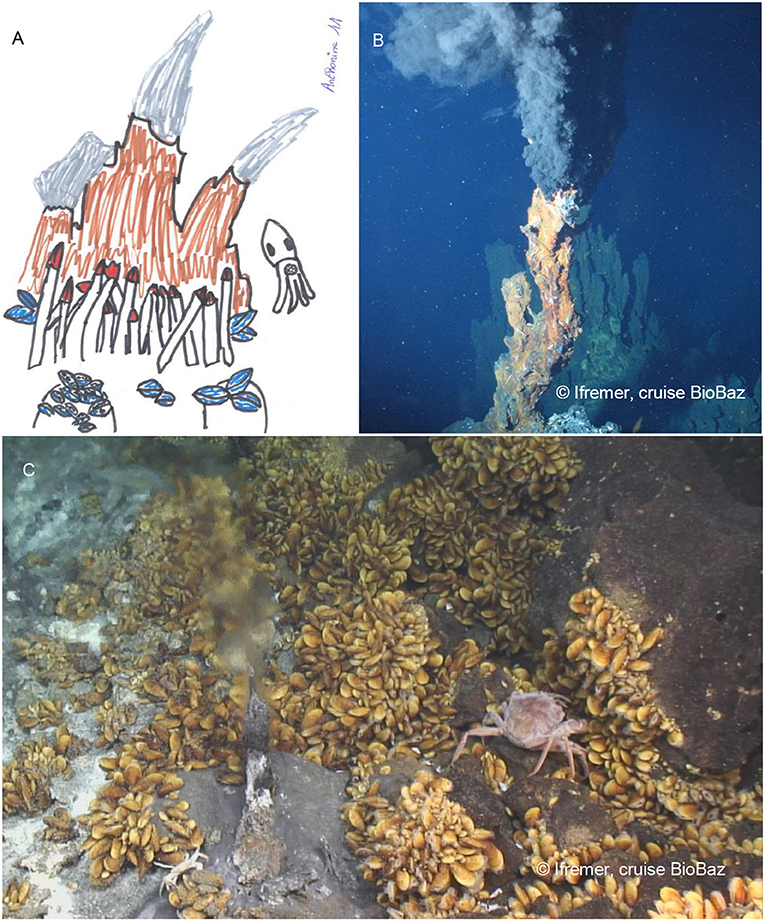
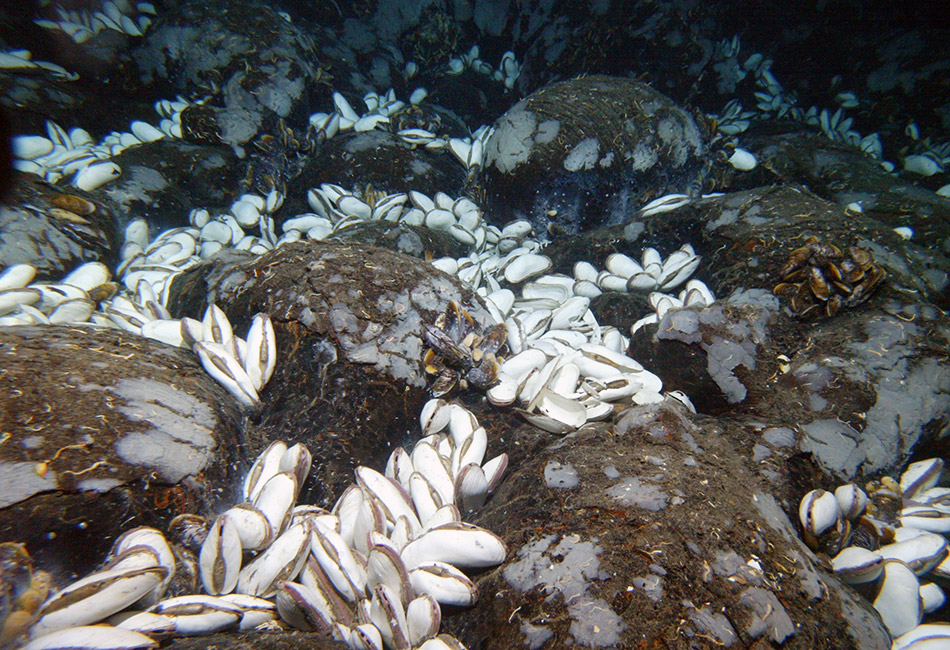
Mussels That Live Near A Deep Sea Vent. The octopi have heads the size of oranges and eat clams mussels crabs and shrimp. Bathymodiolus thermophilus is a species of large deep water mussel a marine bivalve mollusc in the family Mytilidae the true mussels. The deep-sea mussel Bathymodiolus puteoserpentis is one of the most prevalent species at Logatchev where they cover hundreds of square meters of ocean floor. These mussels are one of the most abundant animals at Logatchev.
 Deep Sea Hydrothermal Vents Worksheet Answers From amazeas.blogspot.com
Deep Sea Hydrothermal Vents Worksheet Answers From amazeas.blogspot.com
As the bacteria bloom there are a large number of filter feeders that exist here feather duster worms mussels and clams and feed on the bacteria in the water. The discovery of an abundance of life around deep-sea hydrothermal vents emitting hot and toxic fluids demonstrated that animals and other organisms could thrive in the dark cold and high-pressure deep oceans. The vent mussel community. They also realized that an entirely unique ecosystem including hundreds of new species existed around the vents. Use the internet to investigate some of the various types of well-known symbiotic relationships between prokaryotes and eukaryotes in the world today. Mussels are among the most studied animals found near hydrothermal vents.
They occur at hydrothermal vents and cold seeps where they are one of the most dominant animals.
Mussels are among the most studied animals found near hydrothermal vents. Mussel is technically used for many types of bivalves living in both freshwater and saltwater ecosystems. The species was discovered at abyssal depths when submersible vehicles such as. Tubeworms never leave their tubes which are made of a hard material called chitin. Deep-sea submersibles were used to sample these mussels and run experiments that showed that they were consuming hydrogen. Deep-Sea Mussels Reveal How Animals Adapt to Hydrothermal Vents and Cold Seeps Among the most remarkable of these animals that can survive in the deep sea are bathymodioline mussels.
 Source: divediscover.whoi.edu
Source: divediscover.whoi.edu
As the bacteria bloom there are a large number of filter feeders that exist here feather duster worms mussels and clams and feed on the bacteria in the water. Tubeworms never leave their tubes which are made of a hard material called chitin. Researchers then sent two remotely operated deep-sea submersibles to sample mussels called Bathymodiolus puteoserpentis. The discovery of an abundance of life around deep-sea hydrothermal vents emitting hot and toxic fluids demonstrated that animals and other organisms could thrive in the dark cold and high-pressure deep oceans. Mussels that live near a deep-sea vent.
 Source: phys.org
Source: phys.org
Mussels are among the most studied animals found near hydrothermal vents. The octopi have heads the size of oranges and eat clams mussels crabs and shrimp. Mussel is an edible bivalve of the family. Tubeworms never leave their tubes which are made of a hard material called chitin. These mussels are in the same family as edible mussels but the Bathymodiolinae have become specialized for living in deep-sea environments over the last 60 million years.
 Source: amazeas.blogspot.com
Source: amazeas.blogspot.com
Bathymodiolus mussels are widespread throughout the worlds oceans. Mussel is technically used for many types of bivalves living in both freshwater and saltwater ecosystems. The discovery of an abundance of life around deep-sea hydrothermal vents emitting hot and toxic fluids demonstrated that animals and other organisms could thrive in the dark cold and high-pressure deep oceans. Kenk Wilson 1985. Brittle stars worms and limpets carpet the outside of vent mussel Bathymodiolus shells living near a hydrothermal vent.
 Source: keralaarticles.blogspot.com
Source: keralaarticles.blogspot.com
Symbiont-containing mussels Mytilidae are found at hydrothermal vents and cold seeps on the ocean floor but it is not known whether these taxa represent an ancient lineage endemic to these. Mussels that live near a deep-sea vent. Kenk Wilson 1985. Tubeworms live around hydrothermal vents along the Mid-Ocean Ridge in the Eastern Pacific Ocean. These mussels are one of the most abundant animals at Logatchev.
 Source: oceanexplorer.noaa.gov
Source: oceanexplorer.noaa.gov
Mussels are among the most studied animals found near hydrothermal vents. The scientists had made a fascinating discoverydeep-sea hydrothermal vents. Despite the extreme temperatures and pressures toxic minerals and lack of sunlight that characterized the deep-sea vent ecosystem the species living. Tubeworms never leave their tubes which are made of a hard material called chitin. The Zoarcid fish is a 2 meter long fish that eats almost anything alive including the giant tube worms.
 Source: hydrothermalventszcrenshaw.weebly.com
Source: hydrothermalventszcrenshaw.weebly.com
Researchers then sent two remotely operated deep-sea submersibles to sample mussels called Bathymodiolus puteoserpentis. Within the ε group there are non-pathogenic chemolithoautotrophic symbiotic ε-Proteobacteria that live within the deep sea vent ecosystem and there are pathogenic ε-Proteobacteria such as Helicobacter and Campylobacter species that infect humans and animals. Mussels that live near a deep-sea vent. Bathymodiolus mussels are widespread throughout the worlds oceans. Below is a sample plausible food chain.
 Source: oceantoday.noaa.gov
Source: oceantoday.noaa.gov
Majority of the edible species live attached to the substrates in the inter-tidal zone. The Zoarcid fish is a 2 meter long fish that eats almost anything alive including the giant tube worms. Mussel is technically used for many types of bivalves living in both freshwater and saltwater ecosystems. Below is a sample plausible food chain. Tubeworms live around hydrothermal vents along the Mid-Ocean Ridge in the Eastern Pacific Ocean.
 Source: microbewiki.kenyon.edu
Source: microbewiki.kenyon.edu
Deep-sea submersibles were used to sample these mussels and run experiments that showed that they were consuming hydrogen. The deep-sea is a vast and complex area and one of the least known on our planet. Bathymodiolus thermophilus is a species of large deep water mussel a marine bivalve mollusc in the family Mytilidae the true mussels. Tubeworms never leave their tubes which are made of a hard material called chitin. Within the ε group there are non-pathogenic chemolithoautotrophic symbiotic ε-Proteobacteria that live within the deep sea vent ecosystem and there are pathogenic ε-Proteobacteria such as Helicobacter and Campylobacter species that infect humans and animals.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
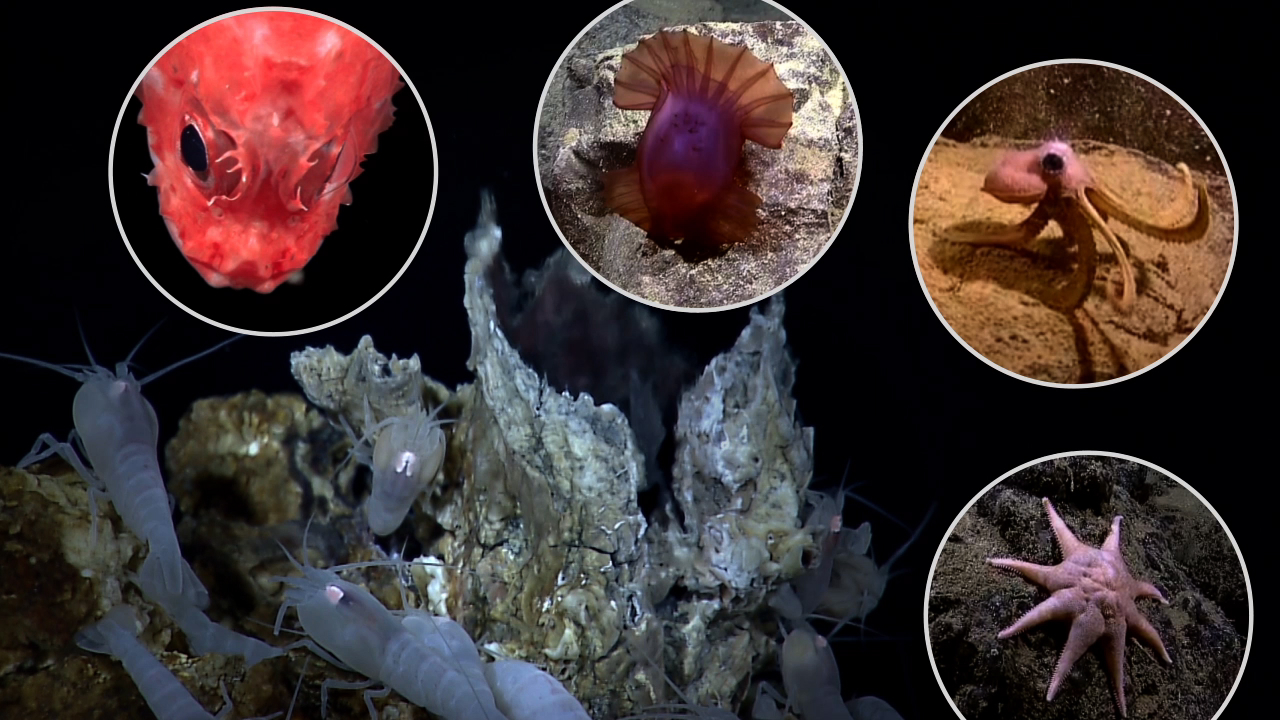
The major predators of the vents are the deep-sea octopus and the zoarcid fish. Use the internet to investigate some of the various types of well-known symbiotic relationships between prokaryotes and eukaryotes in the world today. Mussels are among the most studied animals found near hydrothermal vents. Deep-sea submersibles were used to sample these mussels and run experiments that showed that they were consuming hydrogen. The major predators of the vents are the deep-sea octopus and the zoarcid fish.
 Source: oceana.org
Source: oceana.org
Some species of mussel prefer to live around deep-sea hydro-dermal vents. They occur at hydrothermal vents and cold seeps where they are one of the most dominant animals. The vent mussel community. Within the ε group there are non-pathogenic chemolithoautotrophic symbiotic ε-Proteobacteria that live within the deep sea vent ecosystem and there are pathogenic ε-Proteobacteria such as Helicobacter and Campylobacter species that infect humans and animals. The species was discovered at abyssal depths when submersible vehicles such as.
 Source: microbewiki.kenyon.edu
Source: microbewiki.kenyon.edu
Tubeworms live around hydrothermal vents along the Mid-Ocean Ridge in the Eastern Pacific Ocean. Some species of mussel prefer to live around deep-sea hydro-dermal vents. Scavengers like crabs and shrimp also are found here along with fish and octopus. Researchers then sent two remotely operated deep-sea submersibles to sample mussels called Bathymodiolus puteoserpentis. Deep-Sea Mussels Reveal How Animals Adapt to Hydrothermal Vents and Cold Seeps Among the most remarkable of these animals that can survive in the deep sea are bathymodioline mussels.
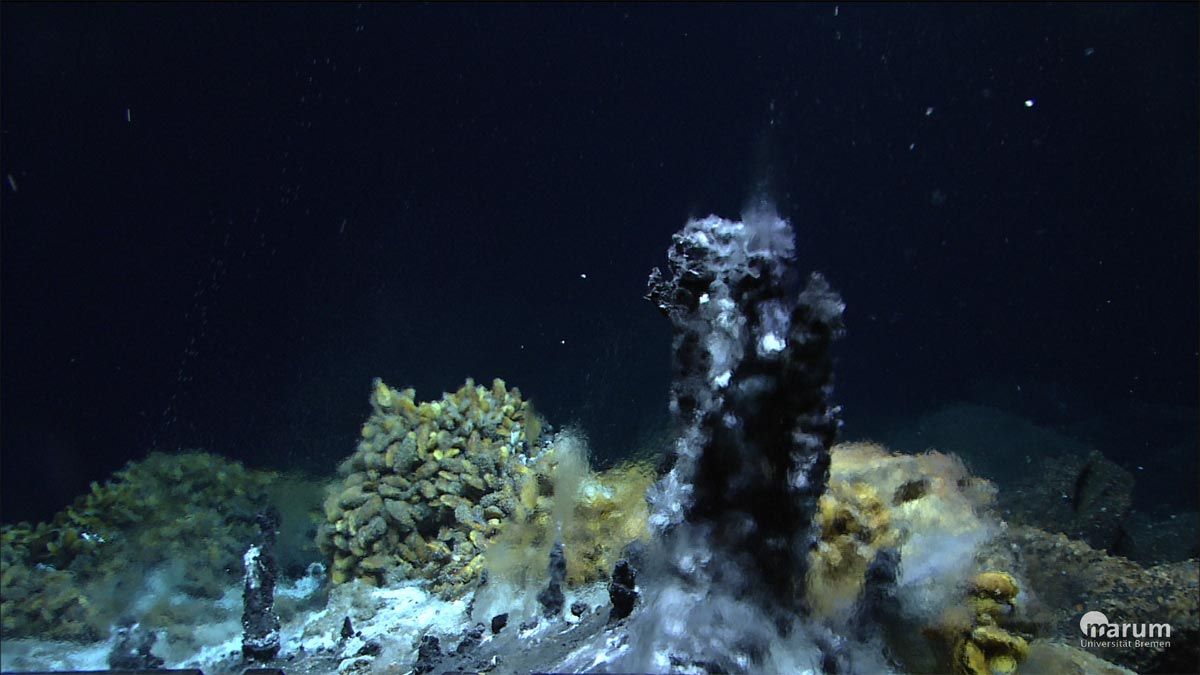 Source: livescience.com
Source: livescience.com
The discovery of an abundance of life around deep-sea hydrothermal vents emitting hot and toxic fluids demonstrated that animals and other organisms could thrive in the dark cold and high-pressure deep oceans. The discovery of an abundance of life around deep-sea hydrothermal vents emitting hot and toxic fluids demonstrated that animals and other organisms could thrive in the dark cold and high-pressure deep oceans. The Zoarcid fish is a 2 meter long fish that eats almost anything alive including the giant tube worms. Some species of mussel prefer to live around deep-sea hydro-dermal vents. Below is a sample plausible food chain.
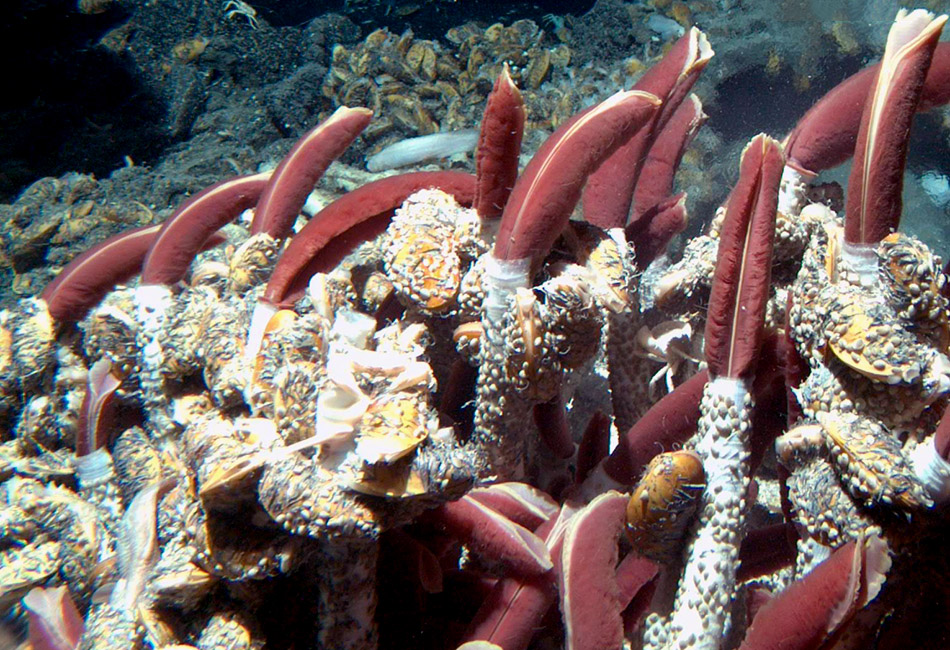 Source: divediscover.whoi.edu
Source: divediscover.whoi.edu
Deep-Sea Mussels Reveal How Animals Adapt to Hydrothermal Vents and Cold Seeps Among the most remarkable of these animals that can survive in the deep sea are bathymodioline mussels. Deep-Sea Mussels Reveal How Animals Adapt to Hydrothermal Vents and Cold Seeps Among the most remarkable of these animals that can survive in the deep sea are bathymodioline mussels. As the bacteria bloom there are a large number of filter feeders that exist here feather duster worms mussels and clams and feed on the bacteria in the water. Hydrothermal vents and methane seeps are extreme deep-sea ecosystems that support dense populations of specialized macrobenthos such as mussels. Mussels are among the most studied animals found near hydrothermal vents.

Majority of the edible species live attached to the substrates in the inter-tidal zone. Despite the extreme temperatures and pressures toxic minerals and lack of sunlight that characterized the deep-sea vent ecosystem the species living. Based on rRNA gene trees the ε-Proteobacteria diverged before the pathogenic ε-Proteobacteria which means that by. The deep-sea is a vast and complex area and one of the least known on our planet. Bathymodiolus mussels are widespread throughout the worlds oceans.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Mussel is technically used for many types of bivalves living in both freshwater and saltwater ecosystems. Within the ε group there are non-pathogenic chemolithoautotrophic symbiotic ε-Proteobacteria that live within the deep sea vent ecosystem and there are pathogenic ε-Proteobacteria such as Helicobacter and Campylobacter species that infect humans and animals. Tubeworms never leave their tubes which are made of a hard material called chitin. Bathymodiolus thermophilus is a species of large deep water mussel a marine bivalve mollusc in the family Mytilidae the true mussels. They also realized that an entirely unique ecosystem including hundreds of new species existed around the vents.
 Source: earthsky.org
Source: earthsky.org
The vent mussel community. Mussels that live near a deep-sea vent. Mussels are among the most studied animals found near hydrothermal vents. The scientists had made a fascinating discoverydeep-sea hydrothermal vents. The discovery of an abundance of life around deep-sea hydrothermal vents emitting hot and toxic fluids demonstrated that animals and other organisms could thrive in the dark cold and high-pressure deep oceans.
 Source: seasky.org
Source: seasky.org
Within the ε group there are non-pathogenic chemolithoautotrophic symbiotic ε-Proteobacteria that live within the deep sea vent ecosystem and there are pathogenic ε-Proteobacteria such as Helicobacter and Campylobacter species that infect humans and animals. Below is a sample plausible food chain. The octopi have heads the size of oranges and eat clams mussels crabs and shrimp. These mussels are in the same family as edible mussels but the Bathymodiolinae have become specialized for living in deep-sea environments over the last 60 million years. Deep-sea submersibles were used to sample these mussels and run experiments that showed that they were consuming hydrogen.
 Source: whoi.edu
Source: whoi.edu
They can grow up to two meters long and ten centimeters in diameter. The deep-sea is a vast and complex area and one of the least known on our planet. Bathymodiolus mussels are widespread throughout the worlds oceans. The discovery of an abundance of life around deep-sea hydrothermal vents emitting hot and toxic fluids demonstrated that animals and other organisms could thrive in the dark cold and high-pressure deep oceans. The octopi have heads the size of oranges and eat clams mussels crabs and shrimp.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title mussels that live near a deep sea vent by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.