Junctional epithelium
Home » » Junctional epitheliumYour Junctional epithelium images are ready in this website. Junctional epithelium are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Download the Junctional epithelium files here. Find and Download all free images.
If you’re looking for junctional epithelium pictures information related to the junctional epithelium topic, you have come to the ideal site. Our site frequently provides you with suggestions for seeing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and locate more informative video content and images that fit your interests.
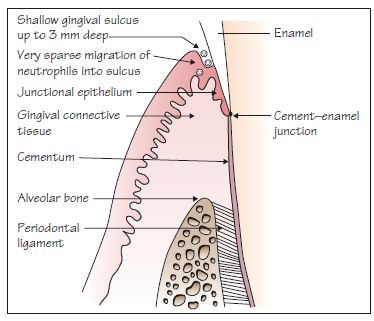
Junctional Epithelium. The junctional epithelium is the epithelial component of the dentogingival unit that is in contact with the tooth surface. It forms a band 23 mm wide around the tooth and is approximately 1530 cells thick coronally and tapers to a single cell apically. Its coronal aspect forms the base of the gingival crevice. Junctional Epithelium The junctional epithelium is the epithelium which is located at the base of the gingival sulcus.
 Pin On Top Doctors From pinterest.com
Pin On Top Doctors From pinterest.com
The junctional epithelium is located at a strategically important interface between the gingival sulcus populated with bacteria and the periodontal soft and mineralized connective tissues that need protection from becoming exposed to bacteria and their products. The junctional epithelium sometimes referenced by the initials JE is the portion of the gingiva or gums that attaches the gums to the enamel or the surface of the tooth. It is the third and most intriguing component of the epithelial integument of the periodontium in addition to the oral gingival epithelium and the oral sulcular epithelium. I INTRODUCTIONT he junctional epithelium is the epithelial component of the dento-gingival unit that is in contact with the tooth surface. Junctional Epithelium The junctional epithelium is the epithelium located at the base of the gingival sulcus. Junctional epithelium a wedge-shaped collar of epithelial cells attached to the tooth surface and to the gingival connective tissue.
F The innermost cells of the junctional epithelium.
The junctional epithelium JE adjacent to the tooth is that part of the gingiva which attaches the connective tissue to the tooth surface Fig. The junctional epithelium JE adjacent to the tooth is that part of the gingiva which attaches the connective tissue to the tooth surface Fig. 1 29 Diagrammatic representation of the four steps in passive eruption af f ording to Gottlieb and Orban4N I Base of the gingival sulcus arrow and the junctional epithelium IE arc on the enamel 2 liase ot the gingival sulcus arrow is on the enamel and part of the junctional epithelium is on the root. Junctional epithelium a wedge-shaped collar of epithelial cells attached to the tooth surface and to the gingival connective tissue. Junctional Epithelium The junctional epithelium is the epithelium located at the base of the gingival sulcus. The junctional epithelium is attached to the tooth surface epithelial attachment by means of an internal basal lamina and to the gingival connective tissue by an external basal lamina that has the same structure as other epithelial-connective tissue attachments elsewhere in the bodyM.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Its coronal aspect forms the base of the gingival crevice. The term junctional epithelium denotes the tissue that is affixed to the tooth on one side and to the oral sulcular epithelium and connective tissue on the other side 17 100. FDevelopment of Junctional epithelium According to Gottlieb the reduced enamel epithelium that covers the crown fuses with the oral epithelium and becomes the Epithelial attachment. Attachment Schroeder and Listgarten 1977. 1 29 Diagrammatic representation of the four steps in passive eruption af f ording to Gottlieb and Orban4N I Base of the gingival sulcus arrow and the junctional epithelium IE arc on the enamel 2 liase ot the gingival sulcus arrow is on the enamel and part of the junctional epithelium is on the root.
 Source: cl.pinterest.com
Source: cl.pinterest.com
What is Junctional Epithelium. The innermost cells of the junctional epithelium form and maintain a tight seal against the mineralized tooth surface the so-called. Epithelial attachment of Gottlieb epithelial attachment Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary Farlex 2012. Mineralized tooth surface the so-called epithelial. The junctional epithelium around implants always originates from epithelial cells of the oral mucosa as opposed to the junctional epithelium around teeth which originates from the reduced enamel epithelium.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Its unique structural and functional adaptation enables the junctional epithelium. Junctional epithelium JE rather than simply providing an attachment to the tooth surface it actively participates in host defense mechanisms. The junctional epithelium JE is the epithelium that is located at the base of the gingival sulcus. The junctional epithelium JE adjacent to the tooth is that part of the gingiva which attaches the connective tissue to the tooth surface Fig. It forms a band 23 mm wide around the tooth and is approximately 1530 cells thick coronally and tapers to a single cell apically.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
1 The key function of JE is to clear and thwart the continuous bacterial challenge by. Hence it is regarded as the most interesting structure of gingiva. Mineralized tooth surface the so-called epithelial. The junctional epithelium is the epithelial. Attachment Schroeder and Listgarten 1977.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The junctional epithelium JE is the epithelium that is located at the base of the gingival sulcus. It forms a band 23 mm wide around the tooth and is approximately 1530 cells thick coronally and tapers to a single cell apically. The junctional epithelium is the epithelial. Apically the junctional epithelium tapers to just a single cell. It is the third and most intriguing component of the epithelial integument of the periodontium in addition to the oral gingival epithelium and the oral sulcular epithelium.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
1 29 Diagrammatic representation of the four steps in passive eruption af f ording to Gottlieb and Orban4N I Base of the gingival sulcus arrow and the junctional epithelium IE arc on the enamel 2 liase ot the gingival sulcus arrow is on the enamel and part of the junctional epithelium is on the root. Junctional Epithelium The junctional epithelium is the epithelium located at the base of the gingival sulcus. Base ot the gingival sulcus arrow is at the cementoenamel line and the. Its unique structural and functional adaptation enables the junctional epithelium. What is Junctional Epithelium.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Junctional Epithelium The junctional epithelium is the epithelium located at the base of the gingival sulcus. The innermost cells of the junctional epithelium form and maintain a tight seal against the mineralized tooth surface the so-called. The junctional epithelium is attached to the tooth surface epithelial attachment by means of an internal basal lamina and to the gingival connective tissue by an external basal lamina that has the same structure as other epithelial-connective tissue attachments elsewhere in the bodyM. Its a thin membrane about 2-3 mm wide around each tooth and is only about 15-30 cells thick coronally. The junctional epithelium JE is the epithelium that is located at the base of the gingival sulcus.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
1 The key function of JE is to clear and thwart the continuous bacterial challenge by. The term junctional epithelium denotes the tissue that is affixed to the tooth on one side and to the oral sulcular epithelium and connective tissue on the other side 17 100. The junctional epithelium JE adjacent to the tooth is that part of the gingiva which attaches the connective tissue to the tooth surface Fig. The junctional epithelium is the epithelial. The junctional epithelium JE is the epithelium that is located at the base of the gingival sulcus.
 Source: fi.pinterest.com
Source: fi.pinterest.com
The junctional epithelium is the epithelial. FDevelopment of Junctional epithelium According to Gottlieb the reduced enamel epithelium that covers the crown fuses with the oral epithelium and becomes the Epithelial attachment. Its unique structural and functional adaptation enables the junctional epithelium. In healthy cases the probe is slowly inserted slides past the sulcular epithelium SE and is stopped by the epithelial attachment EA. 1 The key function of JE is to clear and thwart the continuous bacterial challenge by.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Contact with the tooth surface. The innermost cells of the junctional epithelium form and maintain a tight seal against the mineralized tooth surface the so-called. It consists of collar like band of stratified squamous nonkeratinizing epithelium. Junctional Epithelium The junctional epithelium is the epithelium which is located at the base of the gingival sulcus. In healthy cases the probe is slowly inserted slides past the sulcular epithelium SE and is stopped by the epithelial attachment EA.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
What is Junctional Epithelium. 1 29 Diagrammatic representation of the four steps in passive eruption af f ording to Gottlieb and Orban4N I Base of the gingival sulcus arrow and the junctional epithelium IE arc on the enamel 2 liase ot the gingival sulcus arrow is on the enamel and part of the junctional epithelium is on the root. Mineralized tooth surface the so-called epithelial. I INTRODUCTIONT he junctional epithelium is the epithelial component of the dento-gingival unit that is in contact with the tooth surface. The innermost cells of the junctional epithelium form and maintain a tight seal against the mineralized tooth surface the so-called.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
In healthy cases the probe is inserted gently slides by the sulcular epithelium SE and stops at the epithelial attachment. Hence it is regarded as the most interesting structure of gingiva. The gingival sulcus probing depth is measured with a calibrated periodontal probe. Junctional epithelium JE rather than simply providing an attachment to the tooth surface it actively participates in host defense mechanisms. A calibrated periodontal probe is used to measure the probing depth of the gingival sulcus.
 Source: co.pinterest.com
Source: co.pinterest.com
FDevelopment of Junctional epithelium According to Gottlieb the reduced enamel epithelium that covers the crown fuses with the oral epithelium and becomes the Epithelial attachment. What is Junctional Epithelium. 1 The key function of JE is to clear and thwart the continuous bacterial challenge by. The junctional epithelium JE is the epithelium that is located at the base of the gingival sulcus. It forms a band 23 mm wide around the tooth and is approximately 1530 cells thick coronally and tapers to a single cell apically.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
It is the third and most intriguing component of the epithelial integument of the periodontium in addition to the oral gingival epithelium and the oral sulcular epithelium. It is the third and most intriguing component of the epithelial integument of the periodontium in addition to the oral gingival epithelium and the oral sulcular epithelium. The junctional epithelium JE is the epithelium that is located at the base of the gingival sulcus. Form and maintain a tight seal against the. Junctional epithelium a wedge-shaped collar of epithelial cells attached to the tooth surface and to the gingival connective tissue.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
The gingival sulcus probing depth is measured with a calibrated periodontal probe. Component of the dento-gingival unit that is in. Junctional epithelium JE rather than simply providing an attachment to the tooth surface it actively participates in host defense mechanisms. Junctional epithelium cells constitutively expressed several types of chemokines and cytokines and the expression of chemokines was augmented by bacterial infection. 1 29 Diagrammatic representation of the four steps in passive eruption af f ording to Gottlieb and Orban4N I Base of the gingival sulcus arrow and the junctional epithelium IE arc on the enamel 2 liase ot the gingival sulcus arrow is on the enamel and part of the junctional epithelium is on the root.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The junctional epithelium JE is the epithelium that is located at the base of the gingival sulcus. The junctional epithelium sometimes referenced by the initials JE is the portion of the gingiva or gums that attaches the gums to the enamel or the surface of the tooth. The junctional epithelium is attached to the tooth surface epithelial attachment by means of an internal basal lamina and to the gingival connective tissue by an external basal lamina that has the same structure as other epithelial-connective tissue attachments elsewhere in the bodyM. A calibrated periodontal probe is used to measure the probing depth of the gingival sulcus. In a healthy situation the probe is gently inserted slides past the sulcular epithelium SE and stops at the epithelial attachment.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
The probing depth of the gingival sulcus is measured using a calibrated periodontal probe. The junctional epithelium sometimes referenced by the initials JE is the portion of the gingiva or gums that attaches the gums to the enamel or the surface of the tooth. FDevelopment of Junctional epithelium According to Gottlieb the reduced enamel epithelium that covers the crown fuses with the oral epithelium and becomes the Epithelial attachment. I INTRODUCTIONT he junctional epithelium is the epithelial component of the dento-gingival unit that is in contact with the tooth surface. In a healthy situation the probe is gently inserted slides past the sulcular epithelium SE and stops at the epithelial attachment.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
In a healthy situation the probe is gently inserted slides past the sulcular epithelium SE and stops at the epithelial attachment. The results indicated that the junctional epithelium is a non-keratinizing non-differentiating fast-renewing epithelium with distensible intercellular spaces that serve as a pathway for an inflammatory exudate and neutrophilic granulocytes as a residence for lymphocytes and monocytes as well as for the inward diffusion of foreign molecules. The junctional epithelium is the epithelial. Junctional Epithelium The junctional epithelium is the epithelium located at the base of the gingival sulcus. In healthy cases the probe is inserted gently slides by the sulcular epithelium SE and stops at the epithelial attachment.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title junctional epithelium by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.