Inward rectifying potassium channel
Home » » Inward rectifying potassium channelYour Inward rectifying potassium channel images are available in this site. Inward rectifying potassium channel are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Inward rectifying potassium channel files here. Get all free images.
If you’re looking for inward rectifying potassium channel images information related to the inward rectifying potassium channel topic, you have pay a visit to the right blog. Our website frequently provides you with suggestions for seeking the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and find more informative video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
Inward Rectifying Potassium Channel. Astrocytes regulate potassium and glutamate homeostasis via inwardly rectifying potassium Kir 41 channels in synapses maintaining normal neural excitability. Flagg and Nichols 2005. Miki and Seino 2005. Prominent expression of Kir41 has been indicated in oligodendrocytes but the extent of expression of other Kir subtypes is unclear.
 Pdf Cardiac Strong Inward Rectifier Potassium Channels Semantic Scholar From semanticscholar.org
Pdf Cardiac Strong Inward Rectifier Potassium Channels Semantic Scholar From semanticscholar.org
Some progress has been made in understanding the contribution of. They contribute to the establishment of highly negative E res and long-lasting action potential plateau in various cells including cardiac myocytes. The inward rectifier K channel in skeletal and cardiac muscle belongs to the Kir2x channel family. Inward rectifying potassium channels Kir are a large family of ion channels that play key roles in ion homeostasis in oligodendrocytes the myelinating cells of the central nervous system CNS. Prominent expression of Kir41 has been indicated in oligodendrocytes but the extent of expression of other Kir subtypes is unclear. They are characterised by the property of inward-rectification which is described as the ability to allow large inward currents and smaller outward currents.
Astrocytes regulate potassium and glutamate homeostasis via inwardly rectifying potassium Kir 41 channels in synapses maintaining normal neural excitability.
Miki and Seino 2005. They contribute to the establishment of highly negative E res and long-lasting action potential plateau in various cells including cardiac myocytes. Inwardly-rectifying potassium channels Kir are the principal class of two-TM domain potassium channels. The G protein-coupled inwardly-rectifying potassium channels GIRKs are a family of lipid-gated inward-rectifier potassium ion channels which are activated opened by the signaling lipid PIP2 and a signal transduction cascade starting with ligand -stimulated G protein-coupled receptors GPCRs. 11p151 is an integral membrane protein and inward-rectifier-type potassium channel. These results suggest that acrolein inhibits light-induced stomatal opening through inhibition of Kin channels in guard cells.
 Source: pnas.org
Source: pnas.org
I K1 is importantly involved in maintaining the resting membrane potential in working contractile myocytes. Butt and Kalsi 2006. The potassium inwardly rectifying channel subfamily J member 11 encoded by KCNJ11. Inward rectifier potassium Kir channels are important for regulating excitability in numerous cell types Nichols and Lopatin 1997. Inwardly-rectifying potassium channels Kir are the principal class of two-TM domain potassium channels.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Inward rectifier potassium Kir channels are important for regulating excitability in numerous cell types Nichols and Lopatin 1997. Butt and Kalsi 2006. They contribute to the establishment of highly negative E res and long-lasting action potential plateau in various cells including cardiac myocytes. I have heard that despite this potassium channel being referred to as an inward rectifying channel that in vitro the channel in fact still transports potassium from the inside to the outside of the cell. I K1 is importantly involved in maintaining the resting membrane potential in working contractile myocytes.
 Source: amjmed.com
Source: amjmed.com
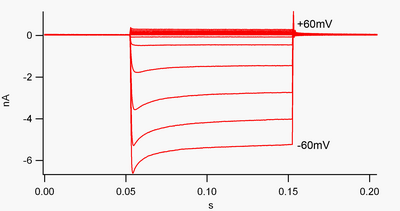
These results suggest that acrolein inhibits light-induced stomatal opening through inhibition of Kin channels in guard cells. They contribute to the establishment of highly negative E res and long-lasting action potential plateau in various cells including cardiac myocytes. Apparently in cardiomyocytes there is an inward rectifying potassium channel that operates during phase 4 of the cardiomyocyte action potential. Inward rectifier potassium channels The inward rectifier K current I K1 is carried by K channels made up of K ir 21 and K ir 22 subunits. However it is largely absent in SAN myocytes.
 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
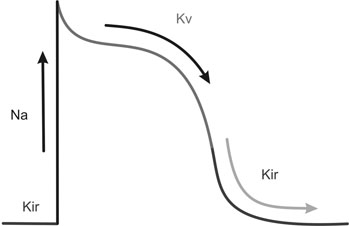
Inward rectifiers are a specialized class of potassium channels that produce large inward currents at potentials negative to the potassium equilibrium potential and only small outward currents at more positive potentials. Apparently in cardiomyocytes there is an inward rectifying potassium channel that operates during phase 4 of the cardiomyocyte action potential. 1 2 GPCRs in turn release activated G-protein βγ- subunits G βγ from inactive heterotrimeric G protein complexes G αβγ. Among eukaryotes they are encoded by the KCNJ gene family. Prominent expression of Kir41 has been indicated in oligodendrocytes but the extent of expression of other Kir subtypes is unclear.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
These results suggest that acrolein inhibits light-induced stomatal opening through inhibition of Kin channels in guard cells. Inwardly rectifying potassium Kir channels were first discovered in 1949 1. Mechanism of rectification in inward-rectifier. Inward rectifiers are a class of K channels that can conduct much larger inward currents at membrane voltages negative to the K equilibrium potential than outward currents at voltages positive to it even when K concentrations on both sides of the membrane are made equal. Inward rectifier potassium Kir channels are important for regulating excitability in numerous cell types Nichols and Lopatin 1997.
 Source: heartrhythmjournal.com
Source: heartrhythmjournal.com
Andersens syndrome AS is a rare and dominantly inherited pathology linked to the inwardly rectifying potassium channel Kir21. Inward rectifiers are a class of K channels that can conduct much larger inward currents at membrane voltages negative to the K equilibrium potential than outward currents at voltages positive to it even when K concentrations on both sides of the membrane are made equal. Mechanism of rectification in inward-rectifier. AS patients exhibit a triad of symptoms that include periodic paralysis cardiac dysrhythmia and bone malformations. I have heard that despite this potassium channel being referred to as an inward rectifying channel that in vitro the channel in fact still transports potassium from the inside to the outside of the cell.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
They facilitate the flow of potassium ions into a cell in response to the hyperpolarization of the cell membrane. Inward rectifiers are a class of K channels that can conduct much larger inward currents at membrane voltages negative to the K equilibrium potential than outward currents at voltages positive to it even when K concentrations on both sides of the membrane are made equal. I K1 is importantly involved in maintaining the resting membrane potential in working contractile myocytes. Inward rectifiers are a specialized class of potassium channels that produce large inward currents at potentials negative to the potassium equilibrium potential and only small outward currents at more positive potentials. Astrocytes regulate potassium and glutamate homeostasis via inwardly rectifying potassium Kir 41 channels in synapses maintaining normal neural excitability.
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
Inward rectifiers are a specialized class of potassium channels that produce large inward currents at potentials negative to the potassium equilibrium potential and only small outward currents at more positive potentials. Inward rectifying potassium channels Kir are a large family of ion channels that play key roles in ion homeostasis in oligodendrocytes the myelinating cells of the central nervous system CNS. They are characterised by the property of inward-rectification which is described as the ability to allow large inward currents and smaller outward currents. Inward rectifier potassium channels The inward rectifier K current I K1 is carried by K channels made up of K ir 21 and K ir 22 subunits. Inwardly rectifying potassium Kir channels were first discovered in 1949 1.
 Source: biorxiv.org
Source: biorxiv.org
Inwardly rectifying potassium Kir channels were first discovered in 1949 1. Butt and Kalsi 2006. Miki and Seino 2005. Inward rectifiers are a class of K channels that can conduct much larger inward currents at membrane voltages negative to the K equilibrium potential than outward currents at voltages positive to it even when K concentrations on both sides of the membrane are made equal. The channels of this family are constitutively active and exhibit strong inward rectification.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
However when the membrane is depolarized there is little to no extracellular flow of potassium ions 2 3 4. The potassium inwardly rectifying channel subfamily J member 11 encoded by KCNJ11. Inwardly-rectifying potassium channels Kir are the principal class of two-TM domain potassium channels. Inward rectifiers are a specialized class of potassium channels that produce large inward currents at potentials negative to the potassium equilibrium potential and only small outward currents at more positive potentials. However it is largely absent in SAN myocytes.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The encoded protein which has a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into a cell rather than out of a cell is controlled by G proteins. The encoded protein which has a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into a cell rather than out of a cell is controlled by G proteins. However it is largely absent in SAN myocytes. Flagg and Nichols 2005. The G protein-coupled inwardly-rectifying potassium channels GIRKs are a family of inward-rectifier potassium ion channels which are activated opened via a signal transduction cascade starting with ligand-stimulated G protein-coupled receptors GPCRs.
 Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
Dhamoon and Jalife 2005. Apparently in cardiomyocytes there is an inward rectifying potassium channel that operates during phase 4 of the cardiomyocyte action potential. The encoded protein which has a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into a cell rather than out of a cell is controlled by G proteins. They are characterised by the property of inward-rectification which is described as the ability to allow large inward currents and smaller outward currents. I have heard that despite this potassium channel being referred to as an inward rectifying channel that in vitro the channel in fact still transports potassium from the inside to the outside of the cell.
 Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
They are characterised by the property of inward-rectification which is described as the ability to allow large inward currents and smaller outward currents. This asymmetry in potassium ion conductance plays a key role in the excitability of muscle cells and neurons. Acrolein at 100 μM inhibited plasma membrane inward-rectifying potassium Kin channels in guard cells. Flagg and Nichols 2005. These results suggest that acrolein inhibits light-induced stomatal opening through inhibition of Kin channels in guard cells.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Acrolein at 100 μM inhibited plasma membrane inward-rectifying potassium Kin channels in guard cells. They facilitate the flow of potassium ions into a cell in response to the hyperpolarization of the cell membrane. Miki and Seino 2005. Apparently in cardiomyocytes there is an inward rectifying potassium channel that operates during phase 4 of the cardiomyocyte action potential. The channels of this family are constitutively active and exhibit strong inward rectification.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Flagg and Nichols 2005. Among eukaryotes they are encoded by the KCNJ gene family. These results suggest that acrolein inhibits light-induced stomatal opening through inhibition of Kin channels in guard cells. The potassium inwardly rectifying channel subfamily J member 11 encoded by KCNJ11. Dhamoon and Jalife 2005.
 Source: molpharm.aspetjournals.org
Source: molpharm.aspetjournals.org
Apparently in cardiomyocytes there is an inward rectifying potassium channel that operates during phase 4 of the cardiomyocyte action potential. This asymmetry in potassium ion conductance plays a key role in the excitability of muscle cells and neurons. I K1 is importantly involved in maintaining the resting membrane potential in working contractile myocytes. They are characterised by the property of inward-rectification which is described as the ability to allow large inward currents and smaller outward currents. Butt and Kalsi 2006.
 Source: wikiwand.com
Source: wikiwand.com
The G protein-coupled inwardly-rectifying potassium channels GIRKs are a family of inward-rectifier potassium ion channels which are activated opened via a signal transduction cascade starting with ligand-stimulated G protein-coupled receptors GPCRs. The inward rectifier K channel in skeletal and cardiac muscle belongs to the Kir2x channel family. The G protein-coupled inwardly-rectifying potassium channels GIRKs are a family of inward-rectifier potassium ion channels which are activated opened via a signal transduction cascade starting with ligand-stimulated G protein-coupled receptors GPCRs. Some progress has been made in understanding the contribution of. Inward rectifier potassium Kir channels are important for regulating excitability in numerous cell types Nichols and Lopatin 1997.
 Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
Some progress has been made in understanding the contribution of. They are characterised by the property of inward-rectification which is described as the ability to allow large inward currents and smaller outward currents. The channels of this family are constitutively active and exhibit strong inward rectification. These results suggest that acrolein inhibits light-induced stomatal opening through inhibition of Kin channels in guard cells. They contribute to the establishment of highly negative E res and long-lasting action potential plateau in various cells including cardiac myocytes.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title inward rectifying potassium channel by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.