Fluorescence quantum yield
Home » » Fluorescence quantum yieldYour Fluorescence quantum yield images are ready in this website. Fluorescence quantum yield are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Fluorescence quantum yield files here. Get all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for fluorescence quantum yield pictures information connected with to the fluorescence quantum yield keyword, you have pay a visit to the right site. Our site always gives you hints for seeking the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and locate more informative video content and images that fit your interests.
Fluorescence Quantum Yield. The fluorescence quantum yield Φ f is a key property that characterizes the ability of a fluorophore to convert absorbed photons into emitted photons under various environmental conditions. F M v and P M can be determined directly but k FM and k IM can only be found indirectly from measurements of the secondary parametersthe fluorescence lifetime τ M andthe fluorescence quantum efficiency q FMwhere k FM q FM τ M and k IM 1-q FM τ M. A molecules efficiency to fluoresce is described by its quantum yield and is defined as the ratio of the number of photons absorbed to the number of photons emitted by a sample. P-terphenyl trans-stilbene anthracene pyrene and α-peryleneThe Φ f is reduced by chemical impurities structural defects and reabsorption of fluorescence.
 Absorption And Emission Peaks And Fluorescence Quantum Yields Of Download Table From researchgate.net
Absorption And Emission Peaks And Fluorescence Quantum Yields Of Download Table From researchgate.net
The fluorescence lifetime τ f emission quantum yield Φ f absorption and emission spectral data of 20 fluorescein derivatives were measured under the same conditions by using time-correlated single photon counting steady state fluorescence and absorption methods to get comparable dataBased on the results the factors and mechanism that control the fluorescence properties of the. A photon of energy hν EM is emitted returning the fluorophore to its ground state S 0. F is a characteristic property of a fluorescent species and is denoted as the ratio of the number of photons emitted through fluorescence to the number of photons absorbed by the fluorophore Equation 1. Fluorescence quantum yield Φ. The quantum yield relates the effic. The absolute method and the relative method.
Fluorescence quantum yield defines the capacity of a fluorophore small molecule or nanoparticle to convert every absorbed photon into an emitted photon ie fluorescence emission.
The fluorescence quantum yield QY of a dye is the fraction of photons absorbed resulting in emission of fluorescence. The fluorescence lifetime τ f emission quantum yield Φ f absorption and emission spectral data of 20 fluorescein derivatives were measured under the same conditions by using time-correlated single photon counting steady state fluorescence and absorption methods to get comparable dataBased on the results the factors and mechanism that control the fluorescence properties of the. We measured the fluorescence quantum yield Φ f of several aromatic hydrocarbon crystals. Since it is difficult to know the precise number of photons absorbed without specialized instrumentation the typical practice of measuring quantum yield depends on. The absolute method and the relative method. There are two methods for measuring the fluorescence quantum yield.
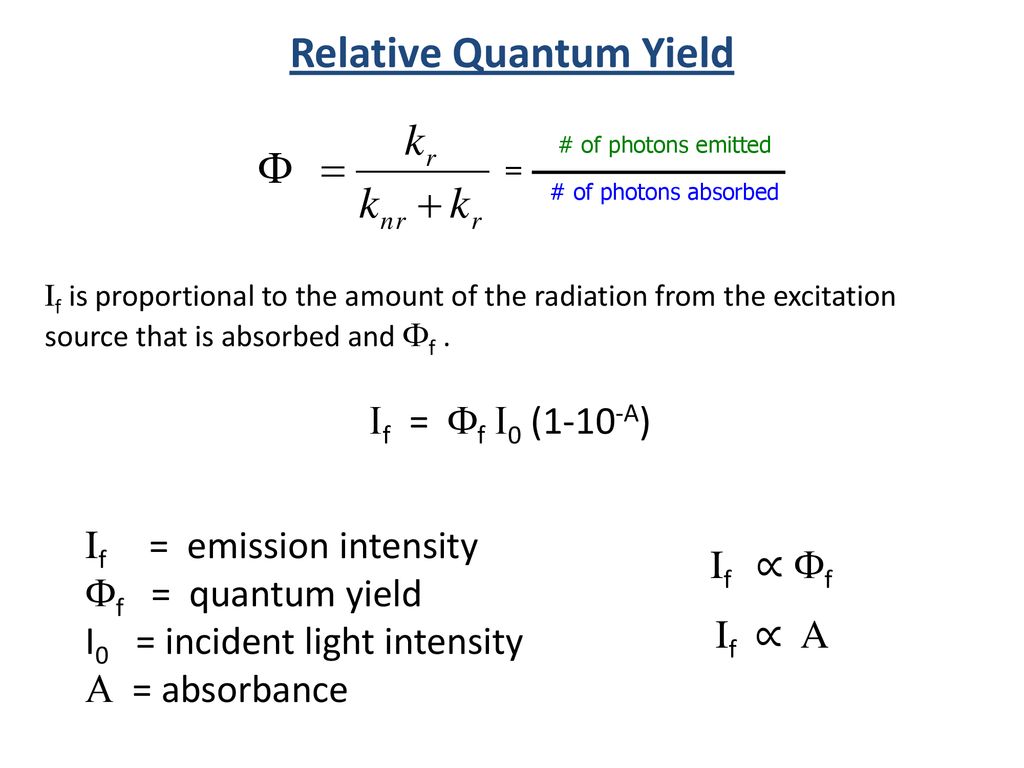 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The quantum yield is an important figure of merit for the optical quality of a fluorophore. F is a characteristic property of a fluorescent species and is denoted as the ratio of the number of photons emitted through fluorescence to the number of photons absorbed by the fluorophore Equation 1. For this purpose we choose rhodamine 101 as a reference dye to measure the nanocrystal fluorescence quantum yield. The fluorescence intensity F is proportional to the amount of light absorbed 5F φI o I where Io is the intensity of the incident light and I is the intensity transmitted. The fluorescence quantum yield QY of a dye is the fraction of photons absorbed resulting in emission of fluorescence.
 Source: horiba.com
Source: horiba.com
However the usefulness of a fluorescent protein depends directly on the quantum yield. To minimize the effect of chemical impurities and structural defects we evaluated the Φ f of highly purified single crystals. The term quantum arises because 1 a photon is a quantum of light and 2 each molecule absorbs one photon. It corresponds to the ratio between the number of photons emitted and the number of photons absorbed. The fluorescence quantum yield φ is the ratio of the number of photons emitted to the number absorbed.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
For this purpose we choose rhodamine 101 as a reference dye to measure the nanocrystal fluorescence quantum yield. In other words the quantum yield gives the probability of the excited state being deactivated by fluorescence rather than by another non-radiative mechanism. The fluorescence quantum yield Φ f D refers to the donor fluorescence quantum yield in the absence of any acceptor. The fluorescence quantum yield QY of a dye is the fraction of photons absorbed resulting in emission of fluorescence. The fluorescence quantum yield ΦF is the ratio of photons absorbed to photons emitted through fluorescence.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The fluorescence quantum yield Φ f D refers to the donor fluorescence quantum yield in the absence of any acceptor. The fluorescence quantum yield Φ f D refers to the donor fluorescence quantum yield in the absence of any acceptor. The Φ f D parameter takes on values from 01 ie 0100. The fluorescence quantum yield which is the ratio of the number of fluorescence photons emitted Stage 3 to the number of photons absorbed Stage 1 is a measure of the relative extent to which these processes occur. The fluorescence quantum yield is defined as the number of photons emitted divided by the number of photons absorbed with an efficiency of 10 being the maximum possi-ble value.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Fluorescence quantum yield defines the capacity of a fluorophore small molecule or nanoparticle to convert every absorbed photon into an emitted photon ie fluorescence emission. For this purpose we choose rhodamine 101 as a reference dye to measure the nanocrystal fluorescence quantum yield. The Φ f D parameter takes on values from 01 ie 0100. The fluorescence quantum yield QY of a dye is the fraction of photons absorbed resulting in emission of fluorescence. The fluorescence quantum yield Φ f is a key property that characterizes the ability of a fluorophore to convert absorbed photons into emitted photons under various environmental conditions.
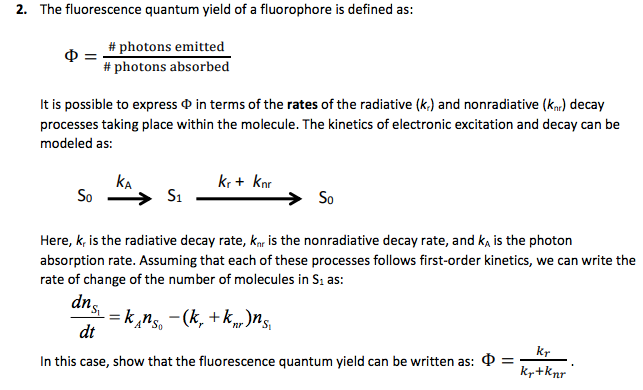 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
To minimize the effect of chemical impurities and structural defects we evaluated the Φ f of highly purified single crystals. Fluorescent proteins are commonly used in cell biology to assess where proteins are within a cell as a function of time and provide insight into intracellular protein function. The fluorescence quantum yield QY of a dye is the fraction of photons absorbed resulting in emission of fluorescence. The fluorescence lifetime τ f emission quantum yield Φ f absorption and emission spectral data of 20 fluorescein derivatives were measured under the same conditions by using time-correlated single photon counting steady state fluorescence and absorption methods to get comparable dataBased on the results the factors and mechanism that control the fluorescence properties of the. Ultimately relates to the.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The quantum yield is an important figure of merit for the optical quality of a fluorophore. In other words the quantum yield gives the probability of the excited state being deactivated by fluorescence rather than by another non-radiative mechanism. However the usefulness of a fluorescent protein depends directly on the quantum yield. There are two methods for measuring the fluorescence quantum yield. For this purpose we choose rhodamine 101 as a reference dye to measure the nanocrystal fluorescence quantum yield.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
The fluorescence quantum yield φ is the ratio of the number of photons emitted to the number absorbed. The fluorescence quantum yield is defined as the number of photons emitted divided by the number of photons absorbed with an efficiency of 10 being the maximum possi-ble value. F is a characteristic property of a fluorescent species and is denoted as the ratio of the number of photons emitted through fluorescence to the number of photons absorbed by the fluorophore Equation 1. Since it is difficult to know the precise number of photons absorbed without specialized instrumentation the typical practice of measuring quantum yield depends on. The fluorescence quantum yield Φ f is a key property that characterizes the ability of a fluorophore to convert absorbed photons into emitted photons under various environmental conditions.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
The quantum yield relates the effic. The term quantum arises because 1 a photon is a quantum of light and 2 each molecule absorbs one photon. It corresponds to the ratio between the number of photons emitted and the number of photons absorbed. The fluorescence quantum yield Φ f D refers to the donor fluorescence quantum yield in the absence of any acceptor. The Φ f D parameter takes on values from 01 ie 0100.

The term fluorescence quantum yield Φ is a measure of the efficiency of photon emission through fluorescence which is the loss of energy by a substance that has absorbed light via emission of a photon. A molecules efficiency to fluoresce is described by its quantum yield and is defined as the ratio of the number of photons absorbed to the number of photons emitted by a sample. The fluorescence quantum yield Φ f D refers to the donor fluorescence quantum yield in the absence of any acceptor. The absolute method and the relative method. F M v and P M can be determined directly but k FM and k IM can only be found indirectly from measurements of the secondary parametersthe fluorescence lifetime τ M andthe fluorescence quantum efficiency q FMwhere k FM q FM τ M and k IM 1-q FM τ M.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
The absolute method and the relative method. For this purpose we choose rhodamine 101 as a reference dye to measure the nanocrystal fluorescence quantum yield. F M v and P M can be determined directly but k FM and k IM can only be found indirectly from measurements of the secondary parametersthe fluorescence lifetime τ M andthe fluorescence quantum efficiency q FMwhere k FM q FM τ M and k IM 1-q FM τ M. The Φ f D parameter takes on values from 01 ie 0100. It can be shown that this definition leads to where k f is the fluorescence rate constant and k i denotes the rate constants of all the decay processes from the first excited state of.
 Source: horiba.com
Source: horiba.com
F M v and P M can be determined directly but k FM and k IM can only be found indirectly from measurements of the secondary parametersthe fluorescence lifetime τ M andthe fluorescence quantum efficiency q FMwhere k FM q FM τ M and k IM 1-q FM τ M. The quantum yield relates the effic. The fluorescence quantum yield φ is the ratio of the number of photons emitted to the number absorbed. The fluorescence quantum yield ΦF is the ratio of photons absorbed to photons emitted through fluorescence. The fluorescence quantum yield is defined as the number of photons emitted divided by the number of photons absorbed with an efficiency of 10 being the maximum possi-ble value.
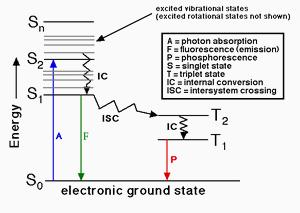 Source: aatbio.com
Source: aatbio.com
Fluorescence quantum yield defines the capacity of a fluorophore small molecule or nanoparticle to convert every absorbed photon into an emitted photon ie fluorescence emission. The fluorescence intensity F is proportional to the amount of light absorbed 5F φI o I where Io is the intensity of the incident light and I is the intensity transmitted. Fluorescence quantum yield Φ. It corresponds to the ratio between the number of photons emitted and the number of photons absorbed. We measured the fluorescence quantum yield Φ f of several aromatic hydrocarbon crystals.
 Source: horiba.com
Source: horiba.com
P-terphenyl trans-stilbene anthracene pyrene and α-peryleneThe Φ f is reduced by chemical impurities structural defects and reabsorption of fluorescence. The fluorescence quantum yield ΦF is the ratio of photons absorbed to photons emitted through fluorescence. Fluorescent proteins are commonly used in cell biology to assess where proteins are within a cell as a function of time and provide insight into intracellular protein function. The absolute method and the relative method. P-terphenyl trans-stilbene anthracene pyrene and α-peryleneThe Φ f is reduced by chemical impurities structural defects and reabsorption of fluorescence.
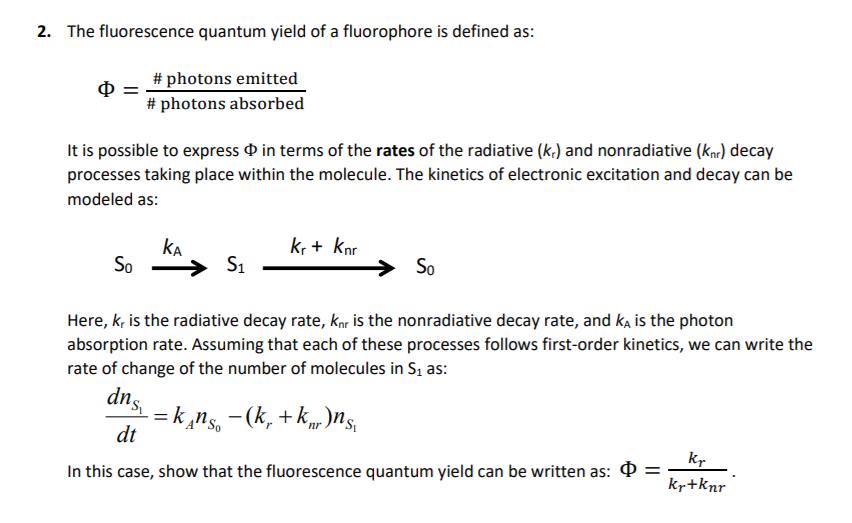 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
The fluorescence quantum yield Φ f is a key property that characterizes the ability of a fluorophore to convert absorbed photons into emitted photons under various environmental conditions. The term fluorescence quantum yield Φ is a measure of the efficiency of photon emission through fluorescence which is the loss of energy by a substance that has absorbed light via emission of a photon. The fluorescence quantum yield Φ f is a key property that characterizes the ability of a fluorophore to convert absorbed photons into emitted photons under various environmental conditions. However the usefulness of a fluorescent protein depends directly on the quantum yield. The Φ f D parameter takes on values from 01 ie 0100.
 Source: horiba.com
Source: horiba.com
The quantum yield is an important figure of merit for the optical quality of a fluorophore. We detail here a simple method to determine the quantum yield of nanocrystals in solution as a function of the absorption. The fluorescence quantum yield Φ f D refers to the donor fluorescence quantum yield in the absence of any acceptor. A molecules efficiency to fluoresce is described by its quantum yield and is defined as the ratio of the number of photons absorbed to the number of photons emitted by a sample. The fluorescence quantum yield φ is the ratio of the number of photons emitted to the number absorbed.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The quantum yield is an important figure of merit for the optical quality of a fluorophore. The fluorescence lifetime τ f emission quantum yield Φ f absorption and emission spectral data of 20 fluorescein derivatives were measured under the same conditions by using time-correlated single photon counting steady state fluorescence and absorption methods to get comparable dataBased on the results the factors and mechanism that control the fluorescence properties of the. The fluorescence quantum yield φ is the ratio of the number of photons emitted to the number absorbed. The fluorescence intensity F is proportional to the amount of light absorbed 5F φI o I where Io is the intensity of the incident light and I is the intensity transmitted. There are two methods for measuring the fluorescence quantum yield.
 Source: horiba.com
Source: horiba.com
A molecules efficiency to fluoresce is described by its quantum yield and is defined as the ratio of the number of photons absorbed to the number of photons emitted by a sample. The fluorescence quantum yield is defined as the number of photons emitted divided by the number of photons absorbed with an efficiency of 10 being the maximum possi-ble value. F M v and P M can be determined directly but k FM and k IM can only be found indirectly from measurements of the secondary parametersthe fluorescence lifetime τ M andthe fluorescence quantum efficiency q FMwhere k FM q FM τ M and k IM 1-q FM τ M. A photon of energy hν EM is emitted returning the fluorophore to its ground state S 0. The fluorescence intensity F is proportional to the amount of light absorbed 5F φI o I where Io is the intensity of the incident light and I is the intensity transmitted.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title fluorescence quantum yield by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.