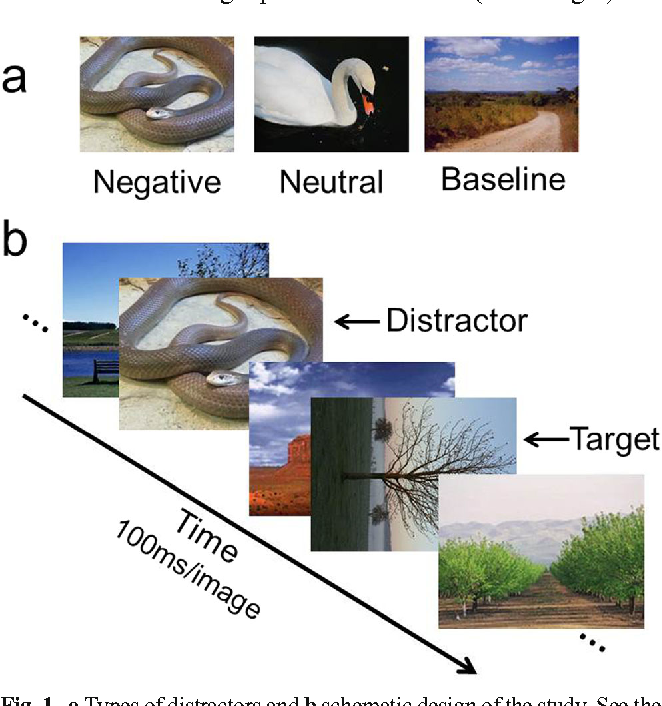
Emotion induced blindness
Home » » Emotion induced blindnessYour Emotion induced blindness images are available. Emotion induced blindness are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Emotion induced blindness files here. Get all free images.
If you’re searching for emotion induced blindness images information linked to the emotion induced blindness topic, you have visit the right site. Our website frequently gives you hints for viewing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly search and find more enlightening video articles and images that fit your interests.
Emotion Induced Blindness. However an emotion-induced blindness effects have been obtained with either emotional cue slows down responding when it misallocates atten- emotional words Arnell et al 2007. Previous findings suggest that emotional stimuli sometimes improve emotion-induced hypervision and sometimes impair emotion-induced blindness the visual perception of subsequent neutral stimuli. The emotional salience of many of the stimuli used to. An ERP study BrianaLKennedy JenniferRawding StevenBMost James E.
 A Example Of Part Of A Typical Emotion Induced Blindness Trial Where Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
A Example Of Part Of A Typical Emotion Induced Blindness Trial Where Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
Hoffman Psychonomic Society Inc. In other words emotion induced blindness and emotional attentional blindness are two different terms for similar concepts and where the EAB also gives in another stimulus that is a verbal stimuli and emotion induced blindness EIB associates with the spatiotemporal competition. 2 All subsequent analyses reflect data from lag 2. However an emotion-induced blindness effects have been obtained with either emotional cue slows down responding when it misallocates atten- emotional words Arnell et al 2007. Fore we operationalized emotion-induced blindness as the difference in accuracy between the neutral and negative conditions at lag 2. Emotion-induced blindness reflects competition at early and late processing stages.
Emotion-induced blindness refers to the impaired awareness for stimuli following an emotional stimulus.
To explore whether effects of valence might diminish once the emotional pictures were no longer surprising we included an examination of whether such effects dif-. The EAB allows for mental. We hypothesized that these differential carryover effects might be due to 2 distinct emotional influences in visual processing. On the one hand emotional stimuli trigger a general enhancement in. An ERP study BrianaLKennedy JenniferRawding StevenBMost James E. Previous findings suggest that emotional stimuli sometimes improve emotion-induced hypervision and sometimes impair emotion-induced blindness the visual perception of subsequent neutral stimuli.
 Source: theconversation.com
Source: theconversation.com
The EAB allows for mental. Superficially EIB appears to be similar to the attentional blink AB a failure to report a target that closely follows another relevant target. Emotion-induced blindness refers to the impaired awareness for stimuli following an emotional stimulus. Ihssen Keil 2008 or tion to an invalid location Fox et al 2001. The emotional salience of many of the stimuli used to.
 Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
Emotion-induced blindness refers to the impaired awareness for stimuli following an emotional stimulus. Suggests that emotion-induced blindness may be distinguishable from closely related phenomena such as the orienting of spatial attention to emotional stimuli or the central resource bottlenecks commonly associated with the attentional blink. We hypothesized that these differential carryover effects might be due to 2 distinct emotional influences in visual processing. The EAB allows for mental. In four experiments using a quickly presented sequence of images they examined how older adults prioritize emotional information.
 Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
Emotion-induced blindness occurs after both negative and positive stimuli in younger adults and is believed to reflect an early spatiotemporal competition between. It has been suggested that valence plays a significant role in driving the perceptual impairment in EIB. Suggests that emotion-induced blindness may be distinguishable from closely related phenomena such as the orienting of spatial attention to emotional stimuli or the central resource bottlenecks commonly associated with the attentional blink. Ihssen Keil 2008 or tion to an invalid location Fox et al 2001. 2 All subsequent analyses reflect data from lag 2.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The emotional attentional blink EAB also known as emotion-induced blindness refers to a phenomenon in which the brief appearance of a task-irrelevant emotionally arousing image captures attention to such an extent that individualscannot detect target stimuli for several hundred ms after the emotional stimulus. However an emotion-induced blindness effects have been obtained with either emotional cue slows down responding when it misallocates atten- emotional words Arnell et al 2007. Hoffman Psychonomic Society Inc. 2014 Abstract Emotion-induced blindness EIB refers to im-paired awareness of items appearing soon after an irrelevant emotionally arousing stimulus. Previous findings suggest that emotional stimuli sometimes improve emotion-induced hypervision and sometimes impair emotion-induced blindness the visual perception of subsequent neutral stimuli.
 Source: scienmag.com
Source: scienmag.com
Emotion-induced blindness EIB refers to impaired awareness of items appearing soon after an irrelevant emotionally arousing stimulus. In other words emotion induced blindness and emotional attentional blindness are two different terms for similar concepts and where the EAB also gives in another stimulus that is a verbal stimuli and emotion induced blindness EIB associates with the spatiotemporal competition. This effect bears resemblance to the attentional blink a phenomenon in which detection of a second target is impaired if it appears soon after the first. USC researchers looked at emotion-induced blindness which refers to distractions caused by emotionally arousing stimuli. Arousal attentional blink conditioning emotion emotion-induced blindness Emotional stimuli attract attention eg Anderson 2005.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Emotion-induced blindness reflects competition at early and late processing stages. Superficially EIB appears to be similar to the attentional blink AB a failure to report a target that closely follows another relevant target. However an emotion-induced blindness effects have been obtained with either emotional cue slows down responding when it misallocates atten- emotional words Arnell et al 2007. The EAB allows for mental. We hypothesized that these differential carryover effects might be due to 2 distinct emotional influences in visual processing.

Emotion-induced blindness EIB refers to impaired awareness of items appearing soon after an irrelevant emotionally arousing stimulus. Suggests that emotion-induced blindness may be distinguishable from closely related phenomena such as the orienting of spatial attention to emotional stimuli or the central resource bottlenecks commonly associated with the attentional blink. Emotion-induced blindness refers to the impaired awareness for stimuli following an emotional stimulus. Emotion-induced blindness occurs after both negative and positive stimuli in younger adults and is believed to reflect an early spatiotemporal competition between. In other words emotion induced blindness and emotional attentional blindness are two different terms for similar concepts and where the EAB also gives in another stimulus that is a verbal stimuli and emotion induced blindness EIB associates with the spatiotemporal competition.
 Source: eurekalert.org
Source: eurekalert.org
This effect bears resemblance to the attentional blink a phenomenon in which detection of a second target is impaired if it appears soon after the first. USC researchers looked at emotion-induced blindness which refers to distractions caused by emotionally arousing stimuli. To explore whether effects of valence might diminish once the emotional pictures were no longer surprising we included an examination of whether such effects dif-. This effect bears resemblance to the attentional blink a phenomenon in which detection of a second target is impaired if it appears soon after the first. Superficially EIB appears to be similar to the attentional blink AB a failure to report a target that closely follows another relevant target.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The emotional attentional blink EAB also known as emotion-induced blindness refers to a phenomenon in which the brief appearance of a task-irrelevant emotionally arousing image captures attention to such an extent that individualscannot detect target stimuli for several hundred ms after the emotional stimulus. Instead we suggest that emotion-induced blindness reflects relatively early competition between targets and. An ERP study BrianaLKennedy JenniferRawding StevenBMost James E. 2014 Abstract Emotion-induced blindness EIB refers to im-paired awareness of items appearing soon after an irrelevant emotionally arousing stimulus. In other words emotion induced blindness and emotional attentional blindness are two different terms for similar concepts and where the EAB also gives in another stimulus that is a verbal stimuli and emotion induced blindness EIB associates with the spatiotemporal competition.

Superficially EIB appears to be similar to the attentional blink AB a failure to report a target that closely follows another relevant target. Emotion-induced blindness occurs after both negative and positive stimuli in younger adults and is believed to reflect an early spatiotemporal competition between. In four experiments using a quickly presented sequence of images they examined how older adults prioritize emotional information. Pes-soa Kastner Ungerleider 2002 thereby increasing the likeli-hood that the emotional information will be used for goal-directed behaviors. Suggests that emotion-induced blindness may be distinguishable from closely related phenomena such as the orienting of spatial attention to emotional stimuli or the central resource bottlenecks commonly associated with the attentional blink.
 Source: pnas.org
Source: pnas.org
Pes-soa Kastner Ungerleider 2002 thereby increasing the likeli-hood that the emotional information will be used for goal-directed behaviors. In other words emotion induced blindness and emotional attentional blindness are two different terms for similar concepts and where the EAB also gives in another stimulus that is a verbal stimuli and emotion induced blindness EIB associates with the spatiotemporal competition. To explore whether effects of valence might diminish once the emotional pictures were no longer surprising we included an examination of whether such effects dif-. This effect bears resemblance to the attentional blink a phenomenon in which detection of a second target is impaired if it appears soon after the first. Ihssen Keil 2008 or tion to an invalid location Fox et al 2001.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
USC researchers looked at emotion-induced blindness which refers to distractions caused by emotionally arousing stimuli. USC researchers looked at emotion-induced blindness which refers to distractions caused by emotionally arousing stimuli. On the one hand emotional stimuli trigger a general enhancement in. Ihssen Keil 2008 or tion to an invalid location Fox et al 2001. View Academics in Emotion induced blindness on Academiaedu.
 Source: medicalxpress.com
Source: medicalxpress.com
Emotion-induced blindness refers to the impaired awareness for stimuli following an emotional stimulus. Fore we operationalized emotion-induced blindness as the difference in accuracy between the neutral and negative conditions at lag 2. Instead we suggest that emotion-induced blindness reflects relatively early competition between targets and. Emotion-induced blindness refers to the impaired awareness for stimuli following an emotional stimulus. Emotion-induced blindness EIB refers to impaired awareness of items appearing soon after an irrelevant emotionally arousing stimulus.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Previous findings suggest that emotional stimuli sometimes improve emotion-induced hypervision and sometimes impair emotion-induced blindness the visual perception of subsequent neutral stimuli. Superficially EIB appears to be similar to the attentional blink AB a failure to report a target that closely follows another relevant target. Ihssen Keil 2008 or tion to an invalid location Fox et al 2001. We hypothesized that these differential carryover effects might be due to 2 distinct emotional influences in visual processing. However an emotion-induced blindness effects have been obtained with either emotional cue slows down responding when it misallocates atten- emotional words Arnell et al 2007.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
In four experiments using a quickly presented sequence of images they examined how older adults prioritize emotional information. However an emotion-induced blindness effects have been obtained with either emotional cue slows down responding when it misallocates atten- emotional words Arnell et al 2007. Hoffman Psychonomic Society Inc. This effect bears resemblance to the attentional blink a phenomenon in which detection of a second target is impaired if it appears soon after the first. Pes-soa Kastner Ungerleider 2002 thereby increasing the likeli-hood that the emotional information will be used for goal-directed behaviors.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
View Academics in Emotion induced blindness on Academiaedu. Previous findings suggest that emotional stimuli sometimes improve emotion-induced hypervision and sometimes impair emotion-induced blindness the visual perception of subsequent neutral stimuli. Emotion Induced Blindness EIB refers to the impairment in the identification of a neutral target image that follows a threatening or fearful distractor image. 2014 Abstract Emotion-induced blindness EIB refers to im-paired awareness of items appearing soon after an irrelevant emotionally arousing stimulus. The EAB allows for mental.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Emotion-induced blindness occurs after both negative and positive stimuli in younger adults and is believed to reflect an early spatiotemporal competition between. In four experiments using a quickly presented sequence of images they examined how older adults prioritize emotional information. Emotion-induced blindness refers to the impaired awareness for stimuli following an emotional stimulus. Ihssen Keil 2008 or tion to an invalid location Fox et al 2001. We hypothesized that these differential carryover effects might be due to 2 distinct emotional influences in visual processing.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Suggests that emotion-induced blindness may be distinguishable from closely related phenomena such as the orienting of spatial attention to emotional stimuli or the central resource bottlenecks commonly associated with the attentional blink. The emotional attentional blink EAB also known as emotion-induced blindness refers to a phenomenon in which the brief appearance of a task-irrelevant emotionally arousing image captures attention to such an extent that individualscannot detect target stimuli for several hundred ms after the emotional stimulus. 2 All subsequent analyses reflect data from lag 2. The EAB allows for mental. Previous findings suggest that emotional stimuli sometimes improve emotion-induced hypervision and sometimes impair emotion-induced blindness the visual perception of subsequent neutral stimuli.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title emotion induced blindness by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.