Can urea cross the cell membrane
Home » » Can urea cross the cell membraneYour Can urea cross the cell membrane images are available. Can urea cross the cell membrane are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Can urea cross the cell membrane files here. Download all free vectors.
If you’re searching for can urea cross the cell membrane pictures information connected with to the can urea cross the cell membrane keyword, you have visit the right site. Our site always provides you with hints for seeking the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and find more enlightening video content and graphics that fit your interests.
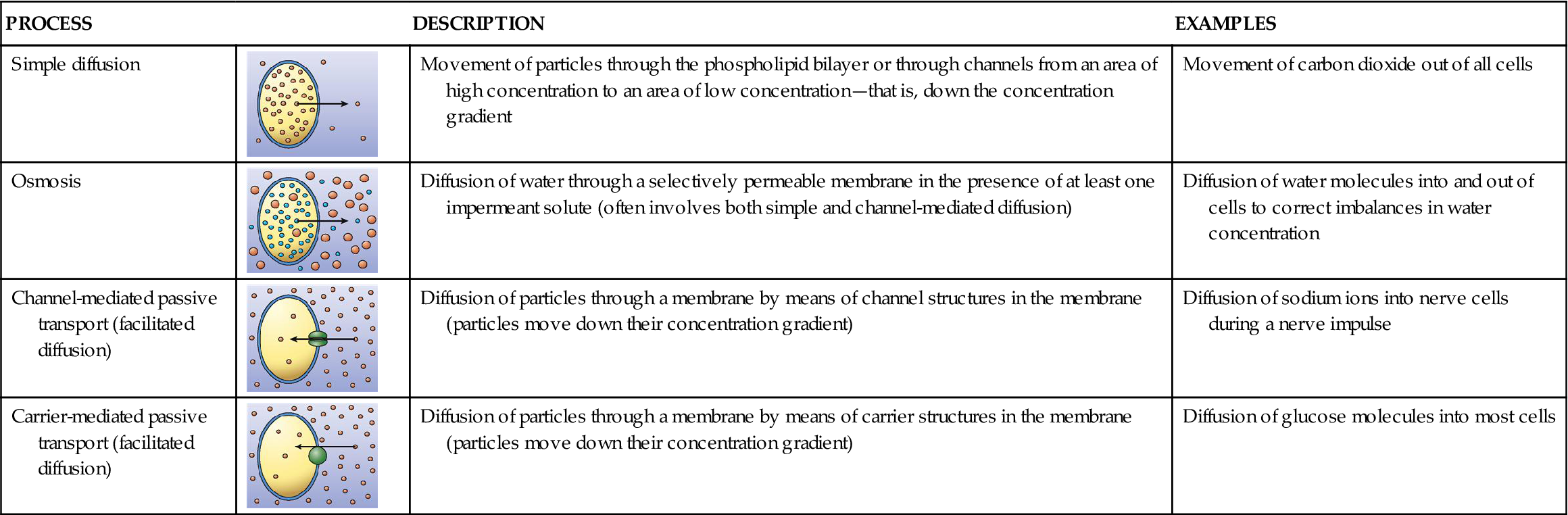
Can Urea Cross The Cell Membrane. Click to see full answer Similarly it is asked how does urea pass through cell membrane. In biology membrane-bound proteins are used for efficient transport across the membrane Brian 2011 from a review of Suc transport in plant cells. Cells can gain or lose water by osmosis. Even after concentration equilibrium is achieved urea molecules will continue to pass through the cell membrane into and out of the cell.
 The Urea Cycle In Diatoms Scheme Showing The Principal Components Of Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
The Urea Cycle In Diatoms Scheme Showing The Principal Components Of Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
Urea has been thought to cross the cell membrane by simple diffusion for 30 years. Even after concentration equilibrium is achieved urea molecules will continue to pass through the cell membrane into and out of the cell. Glycerol is lipid soluble so it diffuses by simple diffusion directly through the cell membrane while glucose is a polar molecule so it diffuses via facilitated diffusion which means it needs a channel protein to work and this means the surface area for the glucose to get in is less than the one for the glycerol. Click to see full answer Similarly it is asked how does urea pass through cell membrane. That doesnt mean that its an easy process because the solubility of water in lipid is about 1 molecule of water per million molecules of lipid. Formerly physiologists taught that very small lipid-insoluble molecules crossed cell membranes.
Urea apparently permeates the red cell membrane via a facilitated diffusion system which plays an important role when red blood cells traverse the renal medulla.
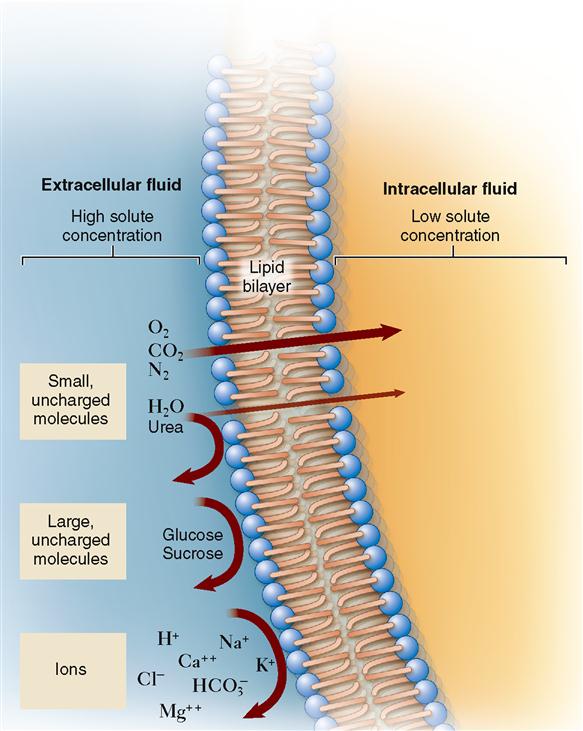
On the other hand it has been shown that urea destabilizes proteins and thus shifts the cell volume regulatory set point towards smaller cell volumes. Transcriptional response to urea Urea is freely permeable through the cell membrane via specific urea transporters so there is no effective osmotic pressure elicited by high concentrations of urea as exist in the renal medulla. Ions are not membrane-permeant. However a permeability study revealed that urea crossing artificial lipid bilayers is actually very low only at 4 10 6 cms Gallucci et al 1971. So in a plant cell sucrose can be moved across the membrane. Water can also pass through the cell membrane by osmosis because of the high osmotic pressure difference between the inside and the outside the cell.
 Source: abpischools.org.uk
Source: abpischools.org.uk
Water can also pass through the cell membrane by osmosis because of the high osmotic pressure difference between the inside and the outside the cell. However a permeability study revealed that urea crossing artificial lipid bilayers is actually very low only at 4 10 6 cms Gallucci et al 1971. Formerly physiologists taught that very small lipid-insoluble molecules crossed cell membranes. Water can move osmotically across the lipid bilayer membrane due to the presence of aquaporin water channels. In biology membrane-bound proteins are used for efficient transport across the membrane Brian 2011 from a review of Suc transport in plant cells.

Water is the main component of the human body and urea is one of the main excretory products of the metabolism of nutrients for cellular energy. Water is the main component of the human body and urea is one of the main excretory products of the metabolism of nutrients for cellular energy. Membrane permeability to large polar molecules is very low. This is enzymatically catalyzed into CO 2 and water which diffuse across the apical membrane into the cell. On the other hand it has been shown that urea destabilizes proteins and thus shifts the cell volume regulatory set point towards smaller cell volumes.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Molecules can move into or out of cells by diffusion and active transport. Water can also pass through the cell membrane by osmosis because of the high osmotic pressure difference between the inside and the outside the cell. Water is the main component of the human body and urea is one of the main excretory products of the metabolism of nutrients for cellular energy. So in a plant cell sucrose can be moved across the membrane. Water can move osmotically across the lipid bilayer membrane due to the presence of aquaporin water channels.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Yes oxygen can pass through easily but active transport and energy ATP are needed to compensate for oxygens non-polarity. Yes oxygen can pass through the cell membrane easily because its small enough in size. In biology membrane-bound proteins are used for efficient transport across the membrane Brian 2011 from a review of Suc transport in plant cells. Urea has been thought to cross the cell membrane by simple diffusion for 30 years. Membrane permeability to large polar molecules is very low.
 Source: brainkart.com
Source: brainkart.com
Ions are not membrane-permeant. So in a plant cell sucrose can be moved across the membrane. Urea apparently permeates the red cell membrane via a facilitated diffusion system which plays an important role when red blood cells traverse the renal medulla. Surprisingly some small polar molecules are capable of permeating the lipid bilayer without the aid of a membrane transport protein. The cell suspension was gently stirred for more than six half-times at room temperature to ensure equilibrium except the extracellular marker 3 Hinulin of 3.
 Source: basicmedicalkey.com
Source: basicmedicalkey.com
Examples include water H 2 O glycerol C 3 H 5 OH 3 urea CH 4 N 2 O and ethanol C 2 H 6 O. Yes oxygen can pass through easily but active transport and energy ATP are needed to compensate for oxygens non-polarity. No oxygen cannot pass through the cell membrane easily because the gas molecule is nonpolar. Transcriptional response to urea Urea is freely permeable through the cell membrane via specific urea transporters so there is no effective osmotic pressure elicited by high concentrations of urea as exist in the renal medulla. That doesnt mean that its an easy process because the solubility of water in lipid is about 1 molecule of water per million molecules of lipid.
 Source: faculty.uncfsu.edu
Source: faculty.uncfsu.edu
Formerly physiologists taught that very small lipid-insoluble molecules crossed cell membranes. Able to cross cell membranes are water and urea. On the other hand it has been shown that urea destabilizes proteins and thus shifts the cell volume regulatory set point towards smaller cell volumes. Urea readily passes cell membranes and does not usually create osmotic gradients across them. In contrast the red blood cell membrane does not contain sucrose transporters and sucrose cannot enter the cell ie the membrane is impermeable to sucrose.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
No oxygen cannot pass through the cell membrane easily because the gas molecule is nonpolar. He glycerol has the whole cell membrane to pass through while glucose has only the channel proteins which do no cover the whole membrane. Formerly physiologists taught that very small lipid-insoluble molecules crossed cell membranes. Membrane permeability to large polar molecules is very low. Water is the main component of the human body and urea is one of the main excretory products of the metabolism of nutrients for cellular energy.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Molecules can move into or out of cells by diffusion and active transport. Examples include water H 2 O glycerol C 3 H 5 OH 3 urea CH 4 N 2 O and ethanol C 2 H 6 O. Water is the main component of the human body and urea is one of the main excretory products of the metabolism of nutrients for cellular energy. Glycerol is lipid soluble so it diffuses by simple diffusion directly through the cell membrane while glucose is a polar molecule so it diffuses via facilitated diffusion which means it needs a channel protein to work and this means the surface area for the glucose to get in is less than the one for the glycerol. The specific group of membrane proteins used for sucrose transport are unimaginatively called Suc transporters SUT.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Cells can gain or lose water by osmosis. Water is the main component of the human body and urea is one of the main excretory products of the metabolism of nutrients for cellular energy. All cells are enclosed by a cell membrane which is selectively permeable. In contrast the red blood cell membrane does not contain sucrose transporters and sucrose cannot enter the cell ie the membrane is impermeable to sucrose. Inside the cell the reverse reaction occurs to produce bicarbonate ions HCO 3.

However the migration in each direction will be the same so that no net change in the urea concentration of the cell occurs. In biology membrane-bound proteins are used for efficient transport across the membrane Brian 2011 from a review of Suc transport in plant cells. Yes oxygen can pass through the cell membrane easily because its small enough in size. However the migration in each direction will be the same so that no net change in the urea concentration of the cell occurs. Glycerol is lipid soluble so it diffuses by simple diffusion directly through the cell membrane while glucose is a polar molecule so it diffuses via facilitated diffusion which means it needs a channel protein to work and this means the surface area for the glucose to get in is less than the one for the glycerol.
 Source: vce.bioninja.com.au
Source: vce.bioninja.com.au
This is enzymatically catalyzed into CO 2 and water which diffuse across the apical membrane into the cell. On the other hand it has been shown that urea destabilizes proteins and thus shifts the cell volume regulatory set point towards smaller cell volumes. Molecules can move into or out of cells by diffusion and active transport. Glycerol is lipid soluble so it diffuses by simple diffusion directly through the cell membrane while glucose is a polar molecule so it diffuses via facilitated diffusion which means it needs a channel protein to work and this means the surface area for the glucose to get in is less than the one for the glycerol. Two of the most important small molecules that need to be able to cross cell membranes are water and urea.
 Source: basicmedicalkey.com
Source: basicmedicalkey.com
In contrast the red blood cell membrane does not contain sucrose transporters and sucrose cannot enter the cell ie the membrane is impermeable to sucrose. Surprisingly some small polar molecules are capable of permeating the lipid bilayer without the aid of a membrane transport protein. Click to see full answer Similarly it is asked how does urea pass through cell membrane. All cells are enclosed by a cell membrane which is selectively permeable. On the other hand it has been shown that urea destabilizes proteins and thus shifts the cell volume regulatory set point towards smaller cell volumes.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Transcriptional response to urea Urea is freely permeable through the cell membrane via specific urea transporters so there is no effective osmotic pressure elicited by high concentrations of urea as exist in the renal medulla. Urea has been thought to cross the cell membrane by simple diffusion for 30 years. On the other hand it has been shown that urea destabilizes proteins and thus shifts the cell volume regulatory set point towards smaller cell volumes. Click to see full answer Similarly it is asked how does urea pass through cell membrane. However the migration in each direction will be the same so that no net change in the urea concentration of the cell occurs.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
However the migration in each direction will be the same so that no net change in the urea concentration of the cell occurs. Two of the most important small molecules that need to be able to cross cell membranes are water and urea. Surprisingly some small polar molecules are capable of permeating the lipid bilayer without the aid of a membrane transport protein. The cell suspension was gently stirred for more than six half-times at room temperature to ensure equilibrium except the extracellular marker 3 Hinulin of 3. However the migration in each direction will be the same so that no net change in the urea concentration of the cell occurs.
 Source: letstalkacademy.com
Source: letstalkacademy.com
Membrane permeability to large polar molecules is very low. Cells can gain or lose water by osmosis. Thus urea easily crosses the cell membrane ie the membrane is permeable to urea driven by the concentration gradient ie extracellular urea intracellular urea. The specific group of membrane proteins used for sucrose transport are unimaginatively called Suc transporters SUT. Urea readily passes cell membranes and does not usually create osmotic gradients across them.

In biology membrane-bound proteins are used for efficient transport across the membrane Brian 2011 from a review of Suc transport in plant cells. Urea apparently permeates the red cell membrane via a facilitated diffusion system which plays an important role when red blood cells traverse the renal medulla. Yes oxygen can pass through the cell membrane easily because its small enough in size. Membrane permeability to large polar molecules is very low. Click to see full answer Similarly it is asked how does urea pass through cell membrane.
 Source: droualb.faculty.mjc.edu
Source: droualb.faculty.mjc.edu
Yes oxygen can pass through easily but active transport and energy ATP are needed to compensate for oxygens non-polarity. However the migration in each direction will be the same so that no net change in the urea concentration of the cell occurs. Click to see full answer Similarly it is asked how does urea pass through cell membrane. Cells can gain or lose water by osmosis. Water can also pass through the cell membrane by osmosis because of the high osmotic pressure difference between the inside and the outside the cell.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title can urea cross the cell membrane by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.