Calcium calmodulin pathway
Home » » Calcium calmodulin pathwayYour Calcium calmodulin pathway images are available. Calcium calmodulin pathway are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Calcium calmodulin pathway files here. Download all free vectors.
If you’re looking for calcium calmodulin pathway pictures information linked to the calcium calmodulin pathway keyword, you have come to the ideal blog. Our website frequently provides you with hints for seeing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and find more enlightening video content and images that match your interests.
Calcium Calmodulin Pathway. CaM is a small protein that contains four EF-hand Ca2 binding sites and is highly conserved among eukaryotes. Calciumcalmodulin Ca2CaM has long been considered a crucial component in wound signaling pathway. One important molecule in these pathways is a protein called calmodulin. Calmodulin CaM is the major Ca 2 sensor of nonmuscle cells 7 and signaling involving calmodulin has been implicated in apoposis 8.
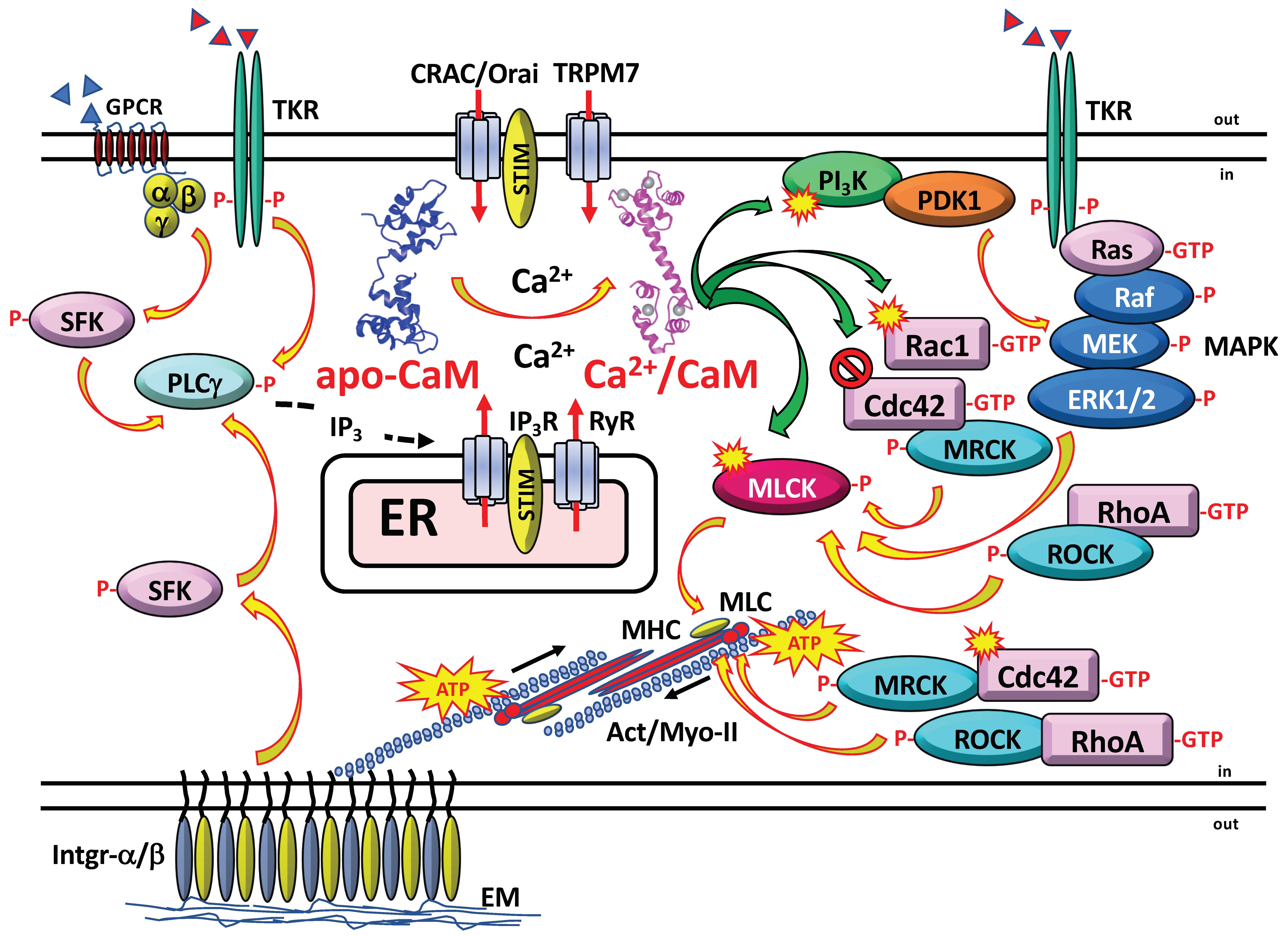 Ijms Free Full Text The Role Of Calmodulin In Tumor Cell Migration Invasiveness And Metastasis Html From mdpi.com
Ijms Free Full Text The Role Of Calmodulin In Tumor Cell Migration Invasiveness And Metastasis Html From mdpi.com
Calmodulin Pathway Concept Id. Calmodulin CaM is the major Ca 2 sensor of nonmuscle cells 7 and signaling involving calmodulin has been implicated in apoposis 8. CaM is a small protein that contains four EF-hand Ca2 binding sites and is highly conserved among eukaryotes. Different signaling mechanisms down-stream from CaM are involved in various types of apoptotic responses including pathways involving calcineurin DAP kinase and calmodulin kinases. CaM is a small protein that contains four EF-hand Ca 2 binding sites and is. Calmodulin or CaM is a polypeptide that is ubiquitous in all eukaryotic cells.
Calmodulin CaM is an intracellular target of the secondary messenger Ca2.
Of calmodulin could be regulated by a ecting the change of intracellular Ca2 concentration and the function of calmodulin might be related to the bodys metabolic process. Calmodulin CaM is an intracellular target of the secondary messenger Ca2. In all organisms in which the CaM gene has been deleted it is essential. An increase in the calcium concentration to approximately 10 -5 M results in the binding of three calcium ions to fungal calmodulin. Calmodulin CaM is the major Ca 2 sensor of nonmuscle cells 7 and signaling involving calmodulin has been implicated in apoposis 8. When Ca 2 binds to calmodulin it forms the Ca 2 calmodulin complex which then interacts with other proteins in the cell.
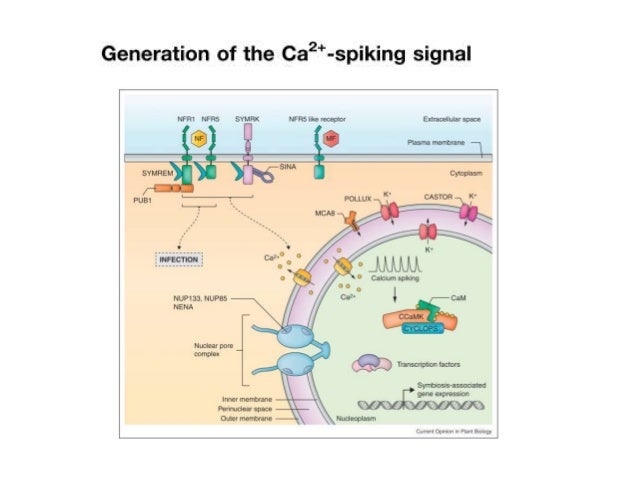 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Perhaps the most universal signaling cascades required for proliferative responses are those initiated by transient rises in intracellular calcium Ca 2The major intracellular receptor for Ca 2 is calmodulin CaM. In order to be activated CaM needs to bind four ions of Ca2. CaM is a small protein that contains four EF-hand Ca 2 binding sites and is. This results in autophosphorylation and complete activation of CAMKK2. Calmodulin is a small calcium-binding protein that participates in the transduction of calcium ions to its effector proteins.
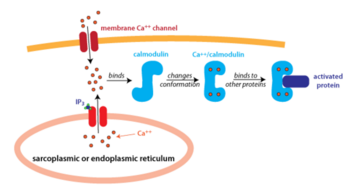
 Source: pancreapedia.org
Source: pancreapedia.org
Calmodulin CaM is an intracellular target of the secondary messenger Ca2. C1516152 The calciumcalmodulin-dependent kinases CaMKs are involved in a large number of cellular responses induced by hormones neurotransmitters and other signaling. We have reported earlier that a family of Ca2CaM-binding transcription factors designated as AtSRs also known as AtCAMTAs can. In vertebrates calcineurin is a heterodimer composed of a catalytic subunit A CnA 5962kDa and a regula-tory subunit B CnB 19kDa. Wang Y et al.

Calcium signaling pathways regulate a multitude of biological process such as transcription cell motility and muscle contraction through diverse cellular response patterns 56. Calmodulin CaM is the major Ca 2 sensor of nonmuscle cells 7 and signaling involving calmodulin has been implicated in apoposis 8. Calmodulin is a small calcium-binding protein that participates in the transduction of calcium ions to its effector proteins. Calmodulin CaM is an intracellular target of the secondary messenger Ca2. Calmodulin is a ubiquitous regulator protein that is involved in many calcium-mediated processes.
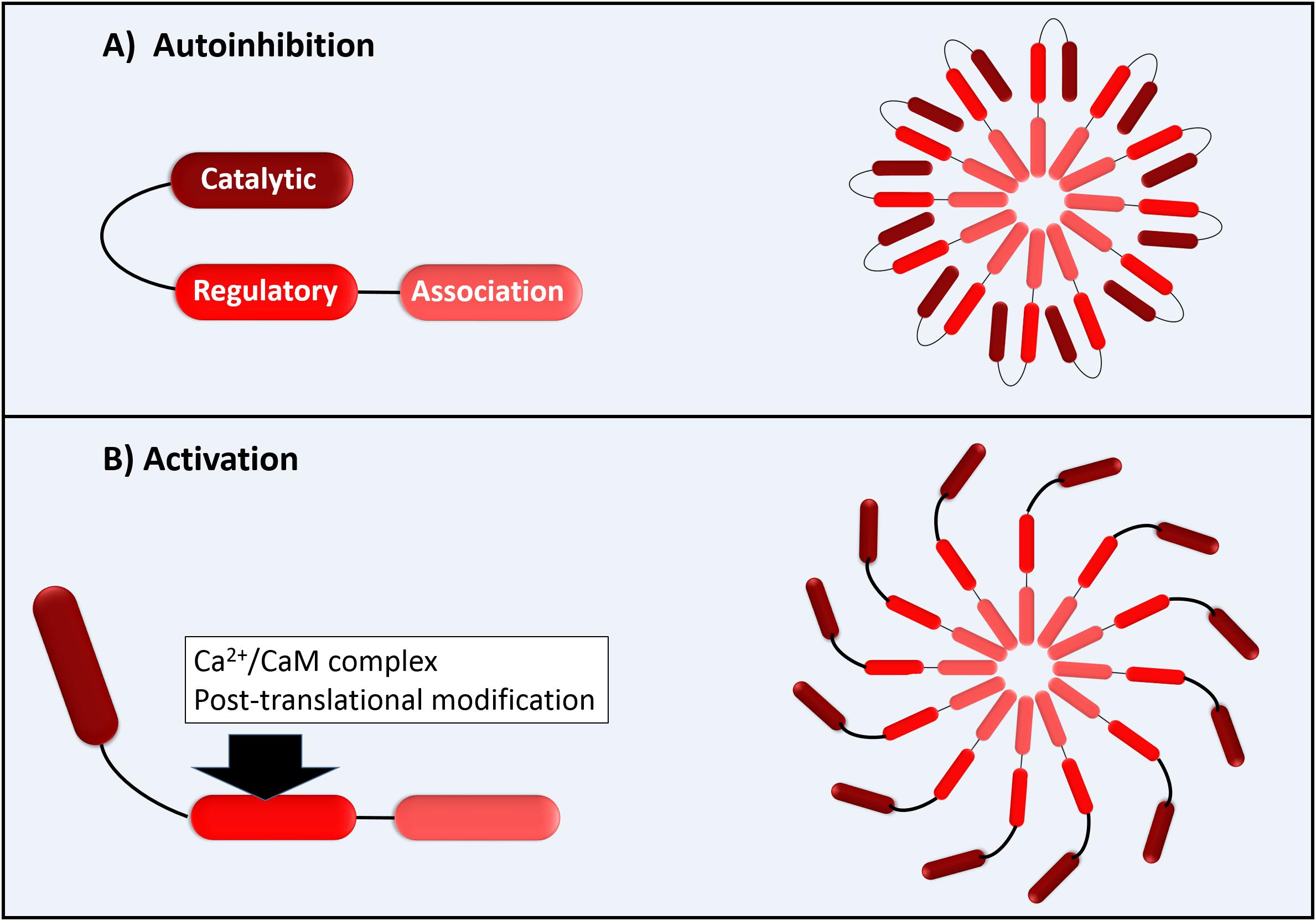
 Source: proteopedia.org
Source: proteopedia.org
18 reported that the Ca2-dependent CaMKK calcium calmodulin kinase kinase signaling pathway is involved in. Calmodulin is a small calcium-binding protein that participates in the transduction of calcium ions to its effector proteins. This results in autophosphorylation and complete activation of CAMKK2. 18 reported that the Ca2-dependent CaMKK calcium calmodulin kinase kinase signaling pathway is involved in. Wang Y et al.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Calmodulin or CaM is a polypeptide that is ubiquitous in all eukaryotic cells. Calmodulin CaM the small and ubiquitous protein expressed from three identical genes in higher organisms is the main cellular calcium Ca2 sensor. CAMKK2 has an autocatalytic site which gets exposed when Ca 2 calmodulin CAM binds to it. This results in autophosphorylation and complete activation of CAMKK2. Of calmodulin could be regulated by a ecting the change of intracellular Ca2 concentration and the function of calmodulin might be related to the bodys metabolic process.
 Source: wikiwand.com
Source: wikiwand.com
Many hormones growth factors and cytokines regulate proliferation of their target cells. However very few Ca2CaM-binding proteins have been identified which regulate plant responses to herbivore attackwounding stress. Calmodulin or CaM is a polypeptide that is ubiquitous in all eukaryotic cells. In order to be activated CaM needs to bind four ions of Ca2. Important effectors are the calciumcalmodulin dependent protein kinases CAMKs and the only calciumcalmodulin dependent protein.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Calciumcalmodulin Ca2CaM has long been considered a crucial component in wound signaling pathway. Calmodulin CaM the small and ubiquitous protein expressed from three identical genes in higher organisms is the main cellular calcium Ca2 sensor. Wang Y et al. An increase in the calcium concentration to approximately 10 -5 M results in the binding of three calcium ions to fungal calmodulin. These proteins are enzymes and effector proteins involved in a variety of cellular and physiological processes.
 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
CaM is a small protein that contains four EF-hand Ca2 binding sites and is highly conserved among eukaryotes. Calmodulin or CaM is a polypeptide that is ubiquitous in all eukaryotic cells. Calmodulin Pathway Concept Id. We have reported earlier that a family of Ca2CaM-binding transcription factors designated as AtSRs also known as AtCAMTAs can. Calcium signaling pathways regulate a multitude of biological process such as transcription cell motility and muscle contraction through diverse cellular response patterns 56.
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
Calmodulin or CaM is a polypeptide that is ubiquitous in all eukaryotic cells. In order to be activated CaM needs to bind four ions of Ca2. CaM is a small protein that contains four EF-hand Ca2 binding sites and is highly conserved among eukaryotes. Calciumcalmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2 CAMKK2 is a serinethreonine-protein kinase belonging to the Ca 2 calmodulin-dependent protein kinase subfamily. Wang Y et al.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
These proteins are enzymes and effector proteins involved in a variety of cellular and physiological processes. We have reported earlier that a family of Ca2CaM-binding transcription factors designated as AtSRs also known as AtCAMTAs can. When Ca 2 binds to calmodulin it forms the Ca 2 calmodulin complex which then interacts with other proteins in the cell. The major intracellular receptor for Ca2 is calmodulin CaM. This results in autophosphorylation and complete activation of CAMKK2.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
In vertebrates calcineurin is a heterodimer composed of a catalytic subunit A CnA 5962kDa and a regula-tory subunit B CnB 19kDa. The CalcineurinNFAT Signaling Pathway Calcineurin PP2B is a calcium-calmodulin-dependent serine threonine phosphatase implicated in a number of biological processes reviewed in refs. The major intracellular receptor for Ca2 is calmodulin CaM. Calcium signaling pathways regulate a multitude of biological process such as transcription cell motility and muscle contraction through diverse cellular response patterns 56. Calmodulin CaM the small and ubiquitous protein expressed from three identical genes in higher organisms is the main cellular calcium Ca2 sensor.
 Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
Calcium signaling pathways regulate a multitude of biological process such as transcription cell motility and muscle contraction through diverse cellular response patterns 56. Wang Y et al. When Ca 2 binds to calmodulin it forms the Ca 2 calmodulin complex which then interacts with other proteins in the cell. An increase in the calcium concentration to approximately 10 -5 M results in the binding of three calcium ions to fungal calmodulin. In vertebrates calcineurin is a heterodimer composed of a catalytic subunit A CnA 5962kDa and a regula-tory subunit B CnB 19kDa.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
These proteins are enzymes and effector proteins involved in a variety of cellular and physiological processes. Calmodulin CaM is the major Ca 2 sensor of nonmuscle cells 7 and signaling involving calmodulin has been implicated in apoposis 8. Calmodulin CaM is an intracellular target of the secondary messenger Ca2. Journal of Molecular Biology 2016. Many hormones growth factors and cytokines regulate proliferation of their target cells.
 Source: biologydictionary.net
Source: biologydictionary.net
Once bound to Ca2 CaM acts as part of a calcium signal transduction pathway by modifying its interactions with various target proteins. Calmodulin is a ubiquitous regulator protein that is involved in many calcium-mediated processes. These proteins are enzymes and effector proteins involved in a variety of cellular and physiological processes. Once bound to Ca2 CaM acts as part of a calcium signal transduction pathway by modifying its interactions with various target proteins. CaM is a small protein that contains four EF-hand Ca2 binding sites and is highly conserved among eukaryotes.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Calmodulin CaM the small and ubiquitous protein expressed from three identical genes in higher organisms is the main cellular calcium Ca2 sensor. This means that it. CaM is a small protein that contains four EF-hand Ca 2 binding sites and is. CaM is a small protein that contains four EF-hand Ca2 binding sites and is highly conserved among eukaryotes. This results in autophosphorylation and complete activation of CAMKK2.
 Source: mpmp.huji.ac.il
Source: mpmp.huji.ac.il
Different signaling mechanisms down-stream from CaM are involved in various types of apoptotic responses including pathways involving calcineurin DAP kinase and calmodulin kinases. An increase in the calcium concentration to approximately 10 -5 M results in the binding of three calcium ions to fungal calmodulin. Calcium signaling pathways regulate a multitude of biological process such as transcription cell motility and muscle contraction through diverse cellular response patterns 56. When Ca 2 binds to calmodulin it forms the Ca 2 calmodulin complex which then interacts with other proteins in the cell. CAMKK2 has an autocatalytic site which gets exposed when Ca 2 calmodulin CAM binds to it.
 Source: jpet.aspetjournals.org
Source: jpet.aspetjournals.org
When Ca 2 binds to calmodulin it forms the Ca 2 calmodulin complex which then interacts with other proteins in the cell. Perhaps the most universal signaling cascades required for proliferative responses are those initiated by transient rises in intracellular calcium Ca 2The major intracellular receptor for Ca 2 is calmodulin CaM. Calmodulin CaM is named because it is a ca lcium mod ulated protein. The CalcineurinNFAT Signaling Pathway Calcineurin PP2B is a calcium-calmodulin-dependent serine threonine phosphatase implicated in a number of biological processes reviewed in refs. Once bound to Ca2 CaM acts as part of a calcium signal transduction pathway by modifying its interactions with various target proteins.
 Source: proteopedia.org
Source: proteopedia.org
We have reported earlier that a family of Ca2CaM-binding transcription factors designated as AtSRs also known as AtCAMTAs can. When Ca 2 binds to calmodulin it forms the Ca 2 calmodulin complex which then interacts with other proteins in the cell. Important effectors are the calciumcalmodulin dependent protein kinases CAMKs and the only calciumcalmodulin dependent protein. Journal of Molecular Biology 2016. CaM is a small protein that contains four EF-hand Ca2 binding sites and is highly conserved among eukaryotes.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title calcium calmodulin pathway by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.